Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
El proyecto interno GEFE está enmarcado en el proyecto coordinado, ESTALLIDOS, financiado por el plan nacional desde el año 2001. El ultimo proyecto aprobado es ESTALLIDOS 6.0 (AYA2016- 79724-C4-2-P). En el proyecto GEFE trabajamos en base al caso científico del proyecto ESTALLIDOS 6.0.
Los estallidos de formación estelar (Starbursts o SB) son clave la evolución de las galaxias y en la historia de formación estelar (FE) del Universo, la producción de metales, y en los procesos de retroalimentación que acoplan las galaxias con la red cósmica. Nuestro proyecto tiene como meta el estudio completo de la física de las regiones masivas del universo local, con objeto de entender el funcionamiento de las galaxias más lejanas y de los SBs más extremos. Combinamos estudios observacionales (usando telescopios terrestres y espaciales) con nuestros modelos teóricos. Entre las instalaciones que usaremos destacan los nuevos instrumentos de GTC, EMIR y MEGARA, en los que el equipo investigador participa y EMIR y MEGARA que entrarán en funcionamiento durante el periodo que cubre este proyecto.
Hemos estructurado nuestra investigación de los próximos tres años alrededor de cinco objetivos:
1) La interacción entre la FS masiva y el medio interestelar.
2) El gas en la formación de las galaxias disco.
3) El papel del entorno en la FS masiva y la evolución de galaxias.
4) Formación estelar en el Universo temprano.
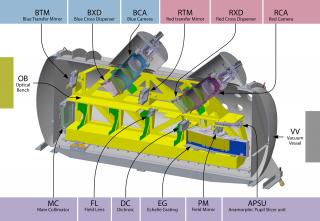
5) Participación en la construcción de nueva instrumentación y en su verificación científica.
Los resultados que esperamos son: i) mejorar la comprensión de la evolución química de las galaxias usando datos de IFUs y modelos bi-dimensionales, ii) entender el papel del gas molecular y los fotones energéticos de fondo, iii) desarrollar una técnica para hacer imagen del gas de la red cósmica que alimenta la formación estelar en galaxias, iv) caracterizar las propiedades químicas y dinámicas del gas que cae sobre las galaxias, v) descifrar las distintas formas en las que fecta a la formación estelar a lo largo de la vida del Universo, prestando especial atención al disparo de la FE en las galaxias con menos metales, vi) explicar como SB masivos evolucionan en modo de 'positive feedback', para entender los SB extremos en el Universo primitivo, vii) estudiar la FS en galaxias Ly-alpha y Ly-break, viii) buscar candidatos a ser estrellas de población III en galaxias extremadamente pobres en metales, locales y a alto 'redshift', ix) desarrollar las técnicas que permitan un uso eficiente de EMIR y MEGARA. Lideraremos casos científicos en los que se usan estos instrumentos, tanto durante la fase de verificación como en su explotación posterior.
Miembros
Resultados
- Se ha descubierto la anticorrelación entre la tasa de formación estelar y la metalicidad del gas en discos de galaxias.
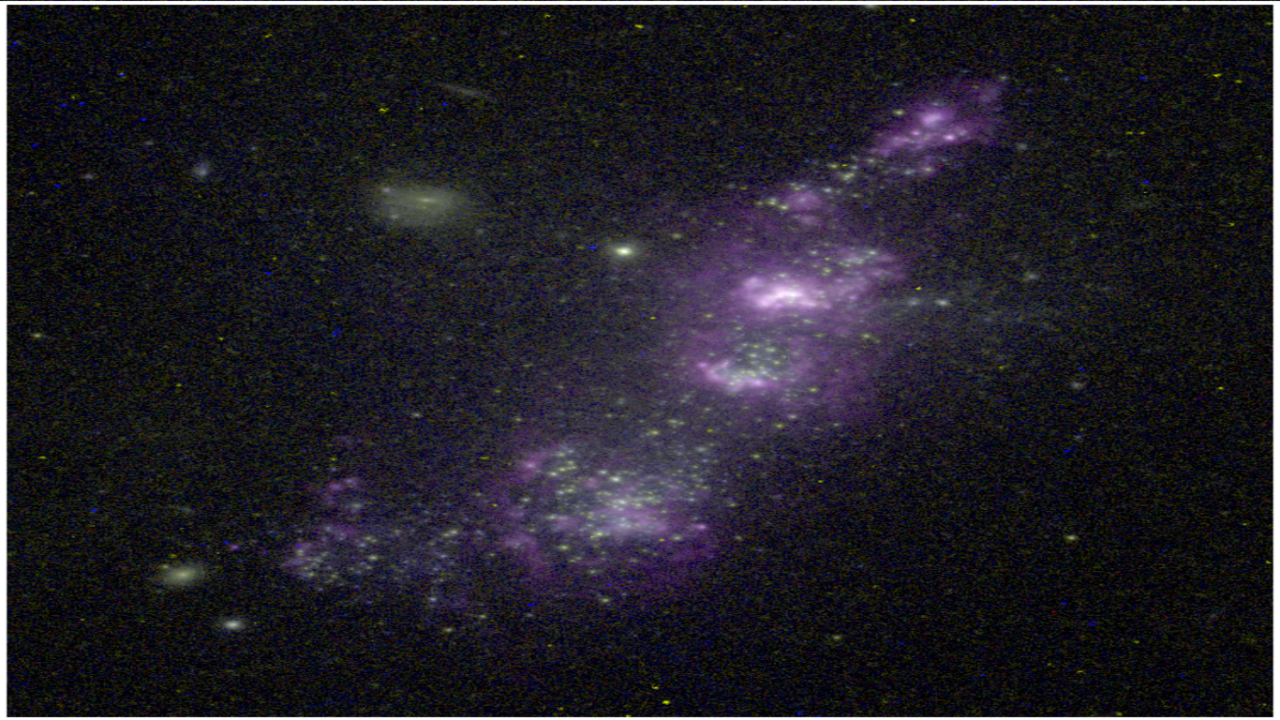
- Descubrimiento una galaxia de baja masa y alta metalicidad, que confirma la estocaticidad de la red cósmica alimentando la formación estelar.
- El polvo producido en las supernovas puede sobrevivir. Los resultados de las simulaciones podrian ser importantes para el universo primitivo.
- El survey SHARDs con sus filtros estrechos permite por primera vez identificar la muestra de galaxias emisoras en Lyman alfa y galaxias con continuo de lyman (lyman break). Se podra estudiar la evolucion entre clases.
- Se identifica un posible AGN binario en la galaxia Mrk 622
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
-
The intrinsic shape of bulges
The J-band structural parameters of a magnitude-limited sample of 148 unbarred S0--Sb galaxies were obtained using the GASP2D algorithm and then analyzed to recover the intrinsic shape of their bulges. We developed a new method to derive the intrinsic shape of bulges based only on photometric data and on the geometrical relationships between the
Corsini, E. M. et al.Fecha de publicación:
32012 -
Probing nuclear activity versus star formation at z ˜ 0.8 using near-infrared multi-object spectroscopy
We present near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopic observations of 28 X-ray and mid-infrared selected sources at a median redshift of z ˜ 0.8 in the Extended Groth Strip (EGS). To date this is the largest compilation of NIR spectra of active galactic nuclei (AGN) at this redshift. The data were obtained using the multi-object spectroscopic mode of the
Rodríguez-Eugenio, N. et al.Fecha de publicación:
32013 -
Characterization of a Sample of Intermediate-type Active Galactic Nuclei. II. Host Bulge Properties and Black Hole Mass Estimates
We present a study of the host bulge properties and their relations with the black hole mass for a sample of 10 intermediate-type active galactic nuclei (AGNs). Our sample consists mainly of early-type spirals, four of them hosting a bar. For 70+10 –17% of the galaxies, we have been able to determine the type of the bulge, and find that these
Benítez, Erika et al.Fecha de publicación:
22013 -
Spectral Energy Distributions of Low-luminosity Radio Galaxies at z ~1-3: A High-z View of the Host/AGN Connection
We study the spectral energy distributions, SEDs (from FUV to MIR bands), of the first sizeable sample of 34 low-luminosity radio galaxies at high redshifts, selected in the COSMOS field. To model the SEDs, we use two different template-fitting techniques: (1) the Hyperz code that only considers single stellar templates and (2) our own developed
Sparks, William B. et al.Fecha de publicación:
12013 -
SHARDS: An Optical Spectro-photometric Survey of Distant Galaxies
We present the Survey for High-z Absorption Red and Dead Sources (SHARDS), an ESO/GTC Large Program carried out using the OSIRIS instrument on the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC). SHARDS is an ultra-deep optical spectro-photometric survey of the GOODS-N field covering 130 arcmin2 at wavelengths between 500 and 950 nm with 24 contiguous medium
Zamorano, Jaime et al.Fecha de publicación:
12013 -
Characterization of a Sample of Intermediate-type AGNs. I. Spectroscopic Properties and Serendipitous Discovery of New Dual AGNs
A sample of 10 nearby intermediate-type active galactic nuclei (AGNs) drawn from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey is presented. The aim of this work is to provide estimations of the black hole (BH) mass for the sample galaxies from the dynamics of the broad-line region. For this purpose, a detailed spectroscopic analysis of the objects was done. Using
Chavushyan, Vahram H. et al.Fecha de publicación:
12013 -
Automated Unsupervised Classification of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Stellar Spectra using k-means Clustering
Large spectroscopic surveys require automated methods of analysis. This paper explores the use of k-means clustering as a tool for automated unsupervised classification of massive stellar spectral catalogs. The classification criteria are defined by the data and the algorithm, with no prior physical framework. We work with a representative set of
Allende-Prieto, C. et al.Fecha de publicación:
12013 -
Constraining clumpy dusty torus models using optimized filter sets
Recent success in explaining several properties of the dusty torus around the central engine of active galactic nuclei has been gathered with the assumption of clumpiness. The properties of such clumpy dusty tori can be inferred by analysing spectral energy distributions (SEDs), sometimes with scarce sampling given that large aperture telescopes
Ramos-Almeida, C. et al.Fecha de publicación:
12013 -
The Nature and Nurture of Bars and Disks
The effects that interactions produce on galaxy disks and how they modify the subsequent formation of bars need to be distinguished to fully understand the relationship between bars and environment. To this aim we derive the bar fraction in three different environments ranging from the field to Virgo and Coma Clusters, covering an unprecedentedly
Méndez-Abreu, J. et al.Fecha de publicación:
122012 -
The Ninth Data Release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: First Spectroscopic Data from the SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey III (SDSS-III) presents the first spectroscopic data from the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS). This ninth data release (DR9) of the SDSS project includes 535,995 new galaxy spectra (median z ~ 0.52), 102,100 new quasar spectra (median z ~ 2.32), and 90,897 new stellar spectra, along with the data
Sheldon, Erin et al.Fecha de publicación:
122012 -
PKS 0347+05: a radio-loud/radio-quiet double active galactic nucleus system triggered in a major galaxy merger
We present optical, infrared (IR) and radio observations of the powerful Fanaroff-Riley type II (FR II) radio source PKS 0347+05 (z = 0.3390), and demonstrate that it is a rare example of a radio-loud/radio-quiet double active galactic nucleus (AGN) system, comprising a weak-line radio galaxy (WLRG) separated by 25 kpc (in projection) from a
Inskip, K. et al.Fecha de publicación:
122012 -
Hubble Space Telescope Hα imaging of star-forming galaxies at z ≃ 1-1.5: evolution in the size and luminosity of giant H II regions
We present Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3 narrow-band imaging of the Hα emission in a sample of eight gravitationally lensed galaxies at z = 1-1.5. The magnification caused by the foreground clusters enables us to obtain a median source plane spatial resolution of 360 pc, as well as providing magnifications in flux ranging from ˜10× to
Livermore, R. C. et al.Fecha de publicación:
112012 -
VLT-VIMOS integral field spectroscopy of luminous and ultraluminous infrared galaxies. I. The sample and first results
Context: (Ultra)Luminous Infrared Galaxies [(U)LIRGs] are much more numerous at cosmological distances than locally, and are likely the precursors of elliptical galaxies. Studies of the physical structure and kinematics of representative samples of these galaxies at low redshift are needed in order to understand the interrelated physical processes
Arribas, S. et al.Fecha de publicación:
32008 -
The environs of the H II region Gum 31
Aims:We analyze the distribution of the interstellar matter in the environs of the H ii region Gum 31, excited by the open cluster NGC 3324, located in the complex Carina region, with the aim of investigating the action of the massive stars on the surrounding neutral material. Methods: We use neutral hydrogen 21-cm line data, radio continuum images
Cappa, C. et al.Fecha de publicación:
12008 -
Filaments in Galactic Winds Driven by Young Stellar Clusters
The starburst galaxy M82 shows a system of Hα-emitting filaments that extend to each side of the galactic disk. We model these filaments as the result of the interaction between the winds from a distribution of super stellar clusters (SSCs). We first derive the condition necessary for producing a radiative interaction between the cluster winds (a
Rodríguez-González, A. et al.Fecha de publicación:
122008 -
Integral field spectroscopy based Hα sizes of local luminous and ultraluminous infrared galaxies. A direct comparison with high-z massive star-forming galaxies
Aims: We study the analogy between local luminous and ultraluminous infrared galaxies (U/LIRGs) and high-z massive star forming galaxies (SFGs) by comparing their basic Hα structural characteristics, such as size and luminosity surface density, in an homogeneous way (i.e. same tracer, size definition, and similar physical scales). Methods: We use
Arribas, S. et al.Fecha de publicación:
52012 -
Extended soft X-ray emission in 3CR radio galaxies at z < 0.3: high excitation and broad line galaxies
We analyze Chandra observations of diffuse soft X-ray emission associated with a complete sample of 3CR radio galaxies at z < 0.3. We focus on the properties of the spectroscopic sub-classes of high excitation galaxies (HEGs) and broad line objects (BLOs). Among the 33 HEGs we detect extended (or possibly extended) emission in about 40% of the
Balmaverde, B. et al.Fecha de publicación:
92012 -
X-ray variability of 104 active galactic nuclei. XMM-Newton power-spectrum density profiles
Context. Active galactic nuclei (AGN), powered by accretion onto supermassive black holes (SMBHs), are thought to be scaled up versions of Galactic black hole X-ray binaries (BH-XRBs). In the past few years evidence of such correspondence include similarities in the broadband shape of the X-ray variability power spectra, with characteristic bend
González-Martín, O. et al.Fecha de publicación:
82012 -
Quiet-Sun Magnetic Field Measurements Based on Lines with Hyperfine Structure
The Zeeman pattern of Mn I lines is sensitive to hyperfine structure (HFS), and because of this, they respond to hectogauss magnetic field strengths differently than the lines commonly used in solar magnetometry. This peculiarity has been employed to measure magnetic field strengths in quiet-Sun regions, assuming the magnetic field to be constant
Sánchez Almeida, J. et al.Fecha de publicación:
32008 -
The GTC project: under commissioning
The GTC (Gran Telescopio Canarias) is an optical/IR telescope, with a 10,4 meter segmented primary, installed at the Observatorio del Roque de Los Muchachos (ORM), at La Palma. Past July 2007 it saw its First Light showing a very promising behaviour. The very good image quality achieved at that an early stage of telescope commissioning is a direct
Alvarez, P. et al.Fecha de publicación:
82008