Astronomy and Astrophysics
Aims: Our long-term project is focused on a few tens of slow rotators with periods of up to 60 h. We aim to obtain their full light curves and reconstruct their spins and shapes. We also precisely scale the models, typically with an accuracy of a few percent.
Methods: We used wide sets of dense light curves for spin and shape reconstructions via light-curve inversion. Precisely scaling them with thermal data was not possible here because of poor infrared datasets: large bodies tend to saturate in WISE mission detectors. Therefore, we recently also launched a special campaign among stellar occultation observers, both in order to scale these models and to verify the shape solutions, often allowing us to break the mirror pole ambiguity.
Results: The presented scheme resulted in shape models for 16 slow rotators, most of them for the first time. Fitting them to chords from stellar occultation timings resolved previous inconsistencies in size determinations. For around half of the targets, this fitting also allowed us to identify a clearly preferred pole solution from the pair of two mirror pole solutions, thus removing the ambiguity inherent to light-curve inversion. We also address the influence of the uncertainty of the shape models on the derived diameters.
Conclusions: Overall, our project has already provided reliable models for around 50 slow rotators. Such well-determined and scaled asteroid shapes will, for example, constitute a solid basis for precise density determinations when coupled with mass information. Spin and shape models in general continue to fill the gaps caused by various biases. Lighcurves are available at the CDS via anonymous ftp to cdsarc.cds.unistra.fr (ftp://130.79.128.5) or via https://cdsarc.cds.unistra.fr/viz-bin/cat/J/A+A/679/A60

Este Proyecto estudia las propiedades físicas y composicionales de los llamados pequeños cuerpos del Sistema Solar, que incluyen asteroides, objetos helados y cometas. Entre los grupos de mayor interés destacan los objetos trans-neptunianos (TNOs), incluyendo los objetos más lejanos detectados hasta la fecha (Extreme-TNOs o ETNOs); los cometas, y
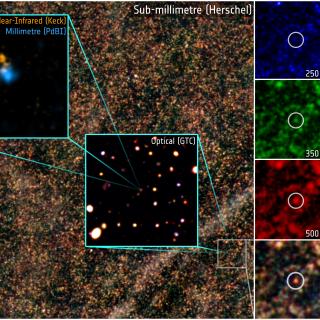
Este grupo desarrolla varios proyectos extragalácticos en diferentes rangos del espectro electromagnético utilizando satélites y telescopios en tierra para estudiar la evolución cosmológica de las galaxias y el origen de la actividad nuclear en galaxias activas. En el aspecto instrumental, el grupo forma parte del consorcio internacional que ha