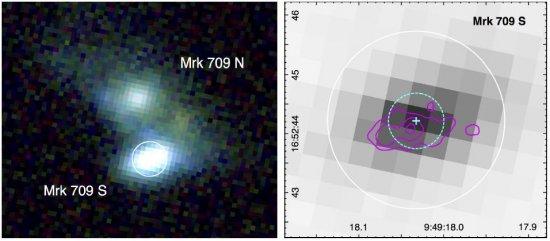
The incidence and properties of present-day dwarf galaxies hosting massive black holes (BHs) can provide important constraints on the origin of high-redshift BH seeds. Here we present high-resolution X-ray and radio observations of the low-metallicity, star-forming, dwarf-galaxy system Mrk 709 with the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA). These data reveal spatially coincident hard X-ray and radio point sources with luminosities suggesting the presence of an accreting massive BH (MBH ∼ 105−7 M⊙). Based on imaging from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), we find that Mrk 709 consists of a pair of compact dwarf galaxies that appear to be interacting with one another. The position of the candidate massive BH is consistent with the optical center of the southern galaxy (Mrk 709 S), while no evidence for an active BH is seen in the northern galaxy (Mrk 709 N). We derive stellar masses of M⋆ ∼2.5×109 M⊙ and M⋆ ∼ 1.1×109 M⊙ for Mrk 709 S and Mrk 709 N, respectively, and present an analysis of the SDSS spectrum of the BH-host Mrk 709 S. At a metallicity of just ∼10% solar, Mrk 709 is among the most metal-poor galaxies with evidence for an active galactic nucleus. Moreover, this discovery adds to the growing body of evidence that massive BHs can form in dwarf galaxies and that deep, high-resolution X-ray and radio observations are ideally suited to reveal accreting massive BHs hidden at optical wavelengths.
Figure CaptionLeft: SDSS image of Mrk 709 (RGB=zrg), which appears to be a pair of interacting dwarf galaxies. We designate the northern and southern galaxies Mrk 709 N and Mrk 709 S. A logarithmic scaling is used to show extended emission. The white circ
Advertised on