It may interest you
-
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on -
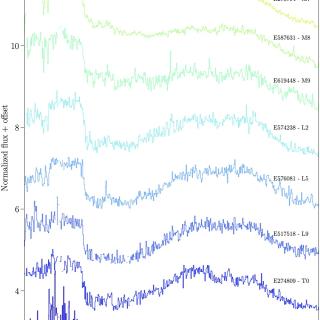 The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on -
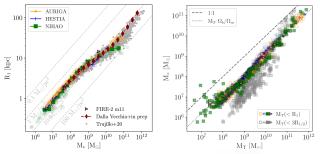 Measuring galaxy sizes is essential for understanding how they were formed and evolved across time. However, traditional methods based on l ight concentration or isophotal densities often lack a clear physical meaning. A recent study from Trujillo+20 explores a more physically motivated definition: the radius R 1, where the stellar surface density falls to 1 solar masses per parsec square —roughly the threshold for gas to form stars in galaxies like the Milky Way. In this work, Arjona-Gálvez+25 uses over 1,000 galaxies from several state-of-the-art cosmological simulations (AURIGA, HESTIAAdvertised on
Measuring galaxy sizes is essential for understanding how they were formed and evolved across time. However, traditional methods based on l ight concentration or isophotal densities often lack a clear physical meaning. A recent study from Trujillo+20 explores a more physically motivated definition: the radius R 1, where the stellar surface density falls to 1 solar masses per parsec square —roughly the threshold for gas to form stars in galaxies like the Milky Way. In this work, Arjona-Gálvez+25 uses over 1,000 galaxies from several state-of-the-art cosmological simulations (AURIGA, HESTIAAdvertised on