El descubrimiento de que las galaxias mas masivas eran mucho mas compactas en el pasado que las galaxias que tienen igual masa hoy, representa uno de los mayores retos para los escenarios actuales que describen la formacion de las galaxias. Una de las ideas que se han sugerido es que estas galaxias compactas se han ido transformado con el tiempo en los núcleos de las galaxias mas masivas que vemos hoy en dia. Nuestro grupo ha llevado a cabo dos estudios paralelos para por un lado tratar de identificar galaxias masivas y compactas que pudieran haber sobrevivido intactas desde su formación inicial y por lo tanto estudiar sus propiedades y otro estudio para explorar la evolución estructural y dinámica de estos objetos a medida que el tiempo transcurre. Hemos encontrado que hoy en dia la poblacion de galaxias masivas y compactas es extremadamente pequeña (<0.03% de las galaxias masivas) y sorprendentemente son objetos relativamente jovenes. Estos resultados sugieren que las galaxias mas masivas se forman siempre de manera compacta y luego evolucionan hasta formar la poblacion actual. Ademas, este analisis nos indica que la evolucion de estos objetos compactos y lejanos debe ser muy rapida pues ya no es posible encontrar ninguno de estas galaxias en la actualidad. Por otro lado, nuestro análisis de la evolución dinamica de los objetos mas masivos es compatible con un escenario donde el halo de materia oscura ya estaba formado en el pasado y el enorme crecimiento observado en tamaño de estos objetos solo se ha producido en la distribución de sus estrellas. En conjunto, nuestros resultados parecen indicar que estas galaxias masivas se formaron en un estallido muy intenso de formación estelar y luego han evolucionado hasta convertirse en el nucleo de las galaxias mas masivas del universo cercano a traves de la acrecion de otras galaxias satelites mas pequeñas.
Advertised on
References
Trujillo, I. et al. (2009). ApJL 692, 118
It may interest you
-
 Type 2 quasars (QSO2s) are active galactic nuclei (AGN) seen through a significant amount of dust and gas that obscures the central supermassive black hole and the broad-line region. Here, we present new mid-infrared spectra of the central kiloparsec of five optically selected QSO2s at redshift z ∼ 0.1 obtained with the Medium Resolution Spectrometer module of the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) aboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). These QSO2s belong to the Quasar Feedback (QSOFEED) sample, and they have bolometric luminosities of log L bol = 45.5 to 46.0 erg s −1 , global starAdvertised on
Type 2 quasars (QSO2s) are active galactic nuclei (AGN) seen through a significant amount of dust and gas that obscures the central supermassive black hole and the broad-line region. Here, we present new mid-infrared spectra of the central kiloparsec of five optically selected QSO2s at redshift z ∼ 0.1 obtained with the Medium Resolution Spectrometer module of the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) aboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). These QSO2s belong to the Quasar Feedback (QSOFEED) sample, and they have bolometric luminosities of log L bol = 45.5 to 46.0 erg s −1 , global starAdvertised on -
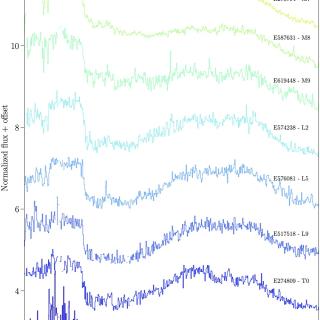 The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on -
 Only a handful of observations truly constrain the nature of dark matter, which is why dozens of different physical models are still viable. Several of the most popular alternatives predict that dark matter halos slowly “thermalize” over time, gradually changing shape and expanding until they form a central region of nearly constant density -- a core. This transformation would not occur if the dark matter particles were completely collision-less, as assumed in the standard model. Therefore, the presence or absence of such a core provides a powerful way to distinguish between the standardAdvertised on
Only a handful of observations truly constrain the nature of dark matter, which is why dozens of different physical models are still viable. Several of the most popular alternatives predict that dark matter halos slowly “thermalize” over time, gradually changing shape and expanding until they form a central region of nearly constant density -- a core. This transformation would not occur if the dark matter particles were completely collision-less, as assumed in the standard model. Therefore, the presence or absence of such a core provides a powerful way to distinguish between the standardAdvertised on
