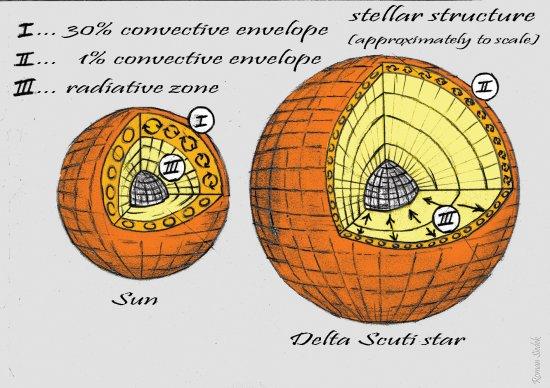
Delta Scuti (δ Sct) stars are opacity-driven pulsators with masses of 1.5-2.5M⊙, their pulsations resulting from the varying ionization of helium. In less massive stars such as the Sun, convection transports mass and energy through the outer 30 per cent of the star and excites a rich spectrum of resonant acoustic modes. Based on the solar example, withno firm theoretical basis, models predict that the convective envelope in δ Sct stars extends only about 1 per cent of the radius, but with sufficient energy to excite solar-like oscillations. This was not observed before the Kepler mission, so the presence of a convective envelope in the models has been questioned. Here we report the detection of solar-like oscillations in the δ Sct star HD 187547, implying that surface convection operates efficiently in stars about twice as massive as the Sun, as the ad hoc models predicted.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
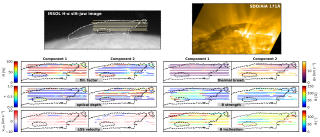 Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on
Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on -
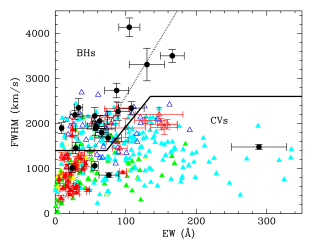 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
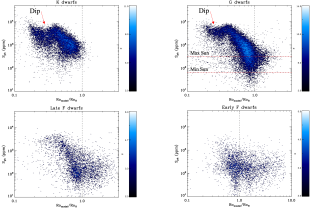 It’s been decades since the need to study other stars to understand the past, present and future of the Sun was realized. One important aspect that has been investigated is the magnetic activity of stars for which we cannot fully grasp the mechanisms involved. Indeed, the origin of stellar magnetic cycles or the dependence of the magnetic activity on the stellar properties are not completely understood. This knowledge improves not only our understanding of the physics involved in stellar evolution but also affects the study of the Sun to better predict high-energy events and the betterAdvertised on
It’s been decades since the need to study other stars to understand the past, present and future of the Sun was realized. One important aspect that has been investigated is the magnetic activity of stars for which we cannot fully grasp the mechanisms involved. Indeed, the origin of stellar magnetic cycles or the dependence of the magnetic activity on the stellar properties are not completely understood. This knowledge improves not only our understanding of the physics involved in stellar evolution but also affects the study of the Sun to better predict high-energy events and the betterAdvertised on