Utilizando modelos semiempíricos de los espectros de fotoabsorción de varios fullerenos individuales (C_80, C_240, C_320 y C_540) predecimos transiciones en la región de la banda difusa más intensa del medio interestelar a 4430 A que podrían explicar su origen, hasta ahora desconocido. Estos modelos también presentan una alta densidad de transiciones en el ultravioleta que reproducen el denominado "bump" a 2175 A en la curva de extinción del medio interestelar (Iglesias-Groth 2004). Parece que los fullerenos podrían ser responsables de dos de los mayores rasgos de la absorción interestelar. Haciendo uso de las secciones eficaces teóricas y de los datos empíricos estimamos que la abundancia de fullerenos es de 0.05 moléculas por millón de átomos de hidrógeno en regiones del medio interestelar con índice de exceso de color E(B-V)~ 1.0.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
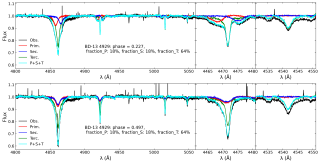 The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on -
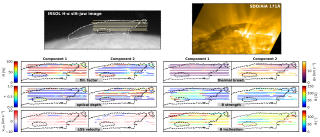 Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on
Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on -
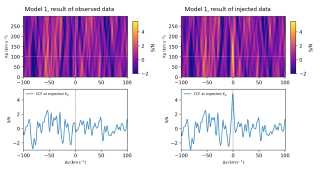 The rocky planet GJ 1132 b, with Earth-like mass and radius, is a prime candidate for atmospheric studies. Previous observations with Hubble and JWST yielded conflicting results about its atmosphere. This study used three transit observations with the CRIRES+ instrument to search for He i, HCN, CH₄, and H₂O in GJ 1132 b's atmosphere. No clear atmospheric signals were detected, but upper limits for CH₄, HCN, and H₂O were established. The results suggest that if GJ 1132 b has an atmosphere, it is not dominated by hydrogen. The work highlights the challenges of detecting high molecular weightAdvertised on
The rocky planet GJ 1132 b, with Earth-like mass and radius, is a prime candidate for atmospheric studies. Previous observations with Hubble and JWST yielded conflicting results about its atmosphere. This study used three transit observations with the CRIRES+ instrument to search for He i, HCN, CH₄, and H₂O in GJ 1132 b's atmosphere. No clear atmospheric signals were detected, but upper limits for CH₄, HCN, and H₂O were established. The results suggest that if GJ 1132 b has an atmosphere, it is not dominated by hydrogen. The work highlights the challenges of detecting high molecular weightAdvertised on