We have selected the Galactic HII region M43, a close-by apparently spherical nebula ionized by a single star (HD37061, B0.5V) to investigate several topics of recent interest in the field of HII regions and massive stars. We perform a combined, comprehensive study of the nebula and its ionizing star by using as many observational constraints as possible. For this study we collected a set of high-quality observations, including the optical spectrum of HD3706, along with nebular optical imaging and long-slit spatially resolved spectroscopy. On the one hand, we have carried out a quantitative spectroscopic analysis of the ionizing star from which we have determined the stellar parameters of HD37061 and the total number of ionizing photons emitted by the star; on the other hand, we have done a empirical analysis of the nebular images and spectroscopy from which we have find observational evidence of scattered light from the Huygens region (the brightest part of the Orion nebula) in the M43 region. We show the importance of an adequate correction of this scattered light in both the imagery and spectroscopic observations of M43 in accurately determining the total nebular Halpha luminosity, the nebular physical conditions. and chemical abundances. We have computed total abundances for three of the analyzed elements (O, S, and N), directly from observable ions (no ionization correction factors are needed). The comparison of these abundances with those derived from the spectrum of the Orion nebula indicates the importance of the atomic data and, specially in the case of M42, the considered ionization correction factors.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
 WISEA J181006.18-101000.5 (WISE1810) is the nearest metal-poor ultracool dwarf to the Sun. It has a low effective temperature and has been classified as an extreme early-T subdwarf. However, methane--the characteristic molecule of the spectral class T--was not detected in the previous low-resolution spectrum. Constraining the metallicity--the abundance of elements heavier than helium-- of these cold objects has been a challenge. Using the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias, the largest optical-infrared telescope in the world, we collected a high-quality near-infrared intermediate-resolutionAdvertised on
WISEA J181006.18-101000.5 (WISE1810) is the nearest metal-poor ultracool dwarf to the Sun. It has a low effective temperature and has been classified as an extreme early-T subdwarf. However, methane--the characteristic molecule of the spectral class T--was not detected in the previous low-resolution spectrum. Constraining the metallicity--the abundance of elements heavier than helium-- of these cold objects has been a challenge. Using the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias, the largest optical-infrared telescope in the world, we collected a high-quality near-infrared intermediate-resolutionAdvertised on -
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on -
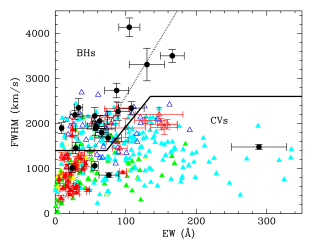 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on