We present a visual determination of the number of bright points (BPs) existing in the quiet Sun, which are structures thought to trace intense kG magnetic concentrations. The measurement is based on a 0farcs1 angular resolution G-band movie obtained with the Swedish Solar Telescope at the solar disk center. We find 0.97 BPs Mm-2, which is a factor 3 larger than any previous estimate. It corresponds to 1.2 BPs per solar granule. Depending on the details of the segmentation, the BPs cover between 0.9% and 2.2% of the solar surface. Assuming their field strength to be 1.5 kG, the detected BPs contribute to the solar magnetic flux with an unsigned flux density between 13 G and 33 G. If network and inter-network regions are counted separately, they contain 2.2 BPs Mm-2 and 0.85 BPs Mm-2, respectively.
Advertised on
References
(2010) Magnetic bright points in the quiet Sun. ApJ, 715, L26
It may interest you
-
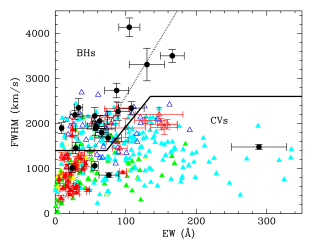 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
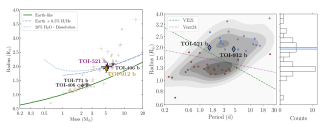 Sub-Neptunes - planets larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune - are the most common type of planet in our Galaxy, yet they are entirely absent from our own Solar System. This absence makes them a major focus for astronomers seeking to understand planetary formation and evolution. We recently conducted an international study, as part of the THIRSTEE project, to characterize two such planets orbiting very similar small, cool stars known as M dwarfs: TOI-521 and TOI-912 . THIRSTEE is an observational-based program that aims to shed light on the sub-Neptune population by providing anAdvertised on
Sub-Neptunes - planets larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune - are the most common type of planet in our Galaxy, yet they are entirely absent from our own Solar System. This absence makes them a major focus for astronomers seeking to understand planetary formation and evolution. We recently conducted an international study, as part of the THIRSTEE project, to characterize two such planets orbiting very similar small, cool stars known as M dwarfs: TOI-521 and TOI-912 . THIRSTEE is an observational-based program that aims to shed light on the sub-Neptune population by providing anAdvertised on -
 In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on
In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on