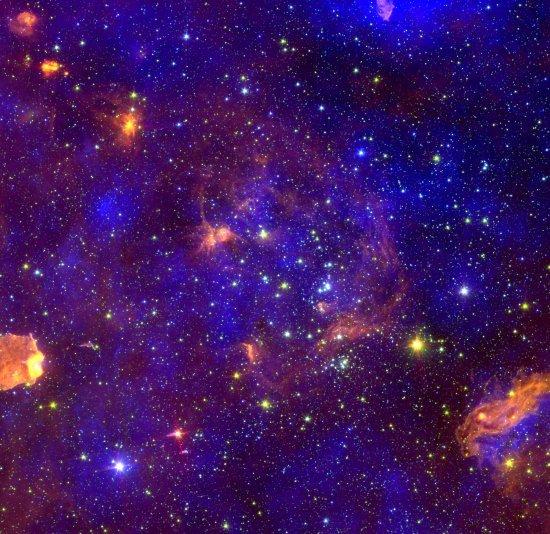
In order to fully understand the gravitational collapse of molecular clouds, the star formation process, and the evolution of circumstellar disks, these phenomena must be studied in different Galactic environments with a range of stellar contents and positions in the Galaxy. The young massive association Cygnus OB2, in the Cygnus-X region, is a unique target to study how star formation and the evolution of circumstellar disks proceed in the presence of a large number of massive stars. We present a catalog obtained with recent optical observations in the r, i, z filters with OSIRIS, mounted on the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio CANARIAS telescope, which is the deepest optical catalog of Cyg OB2 to date. The catalog consists of 64,157 sources down to M = 0.15 M ☉ at the adopted distance and age of Cyg OB2. A total of 38,300 sources have good photometry in all three bands. We combined the optical catalog with existing X-ray data of this region, in order to define the cluster locus in the optical diagrams. The cluster locus in the r – i versus i – z diagram is compatible with an extinction of the optically selected cluster members in the 2.64 m < AV < 5.57 m range. We derive an extinction map of the region, finding a median value of AV = 4.33 m in the center of the association, decreasing toward the northwest. In the color-magnitude diagrams, the shape of the distribution of main-sequence stars is compatible with the presence of an obscuring cloud in the foreground ~850 ± 25 pc from the Sun.
Advertised on
References
2012 ApJS, 202, 19
It may interest you
-
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on -
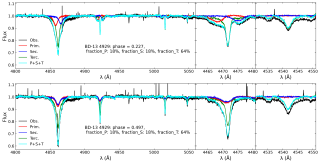 The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on -
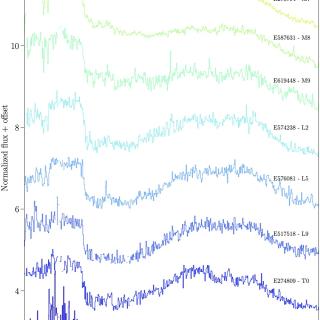 The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
