The hypothesis of a universal initial mass function (IMF) - motivated by observations in nearby stellar systems - has been recently challenged by the discovery of a systematic variation of the IMF with the centralvelocity dispersion, σ, of early-type galaxies (ETGs), towards an excessof low-mass stars in high-σ galaxies. This trend has been derived so farfrom integrated spectra, and remains unexplained at present. To testwhether such trend depends on the local properties within a galaxy, we have obtained new, extremely deep, spectroscopic data, for three nearby ETGs, two galaxies with high σ (~300 km/s), and one lower mass system, with σ ~100 km/s. From the analysis of IMF-sensitive spectral features, we find that the IMF depends significantly ongalactocentric distance in the massive ETGs, with the enhanced fraction of low-mass stars mostly confined to their central regions. In contrast, the low-σ galaxy does not show any significant radial gradient in the IMF, well described by a shallower distribution, relative to the innermost regions of massive galaxies, at all radii. Such a result indicates that the IMF should be regarded as a local (rather than global) property, and suggests a significant difference between the formation process of the core and the outer regions ofmassive ETGs
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on -
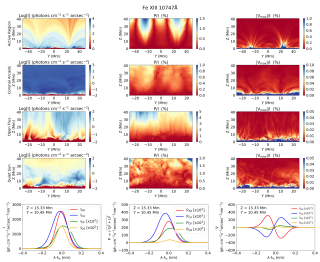 The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on
The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on -
 In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on
In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on