The best spectrographs are limited in stability by their calibration light source. Laser frequency combs are the ideal calibrators for astronomical spectrographs. They emit a spectrum of lines that are equally spaced in frequency and that are as accurate and stable as the atomic clock relative to which the comb is stabilized. Absolute calibration provides the radial velocity of an astronomical object relative to the observer (on Earth). For the detection of Earth-mass exoplanets in Earth-like orbits around solar-type stars, or of cosmic acceleration, the observable is a tiny velocity change of less than 10 cm s-1, where the repeatability of the calibration – the variation in stability across observations – is important. Hitherto, only laboratory systems or spectrograph calibrations of limited performance have been demonstrated. Here we report the calibration of an astronomical spectrograph with a short-term Doppler shift repeatability of 2.5 cm s-1, and use it to monitor the star HD75289 and recompute the orbit of its planet. This repeatability should make it possible to detect Earth-like planets in the habitable zone of star or even to measure the cosmic acceleration directly.
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
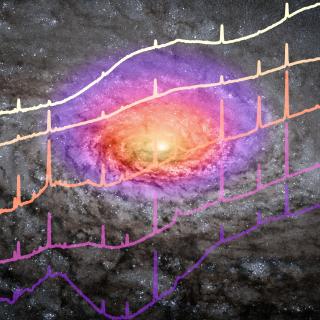 Type 2 quasars (QSO2s) are active galactic nuclei (AGN) seen through a significant amount of dust and gas that obscures the central supermassive black hole and the broad-line region. Here, we present new mid-infrared spectra of the central kiloparsec of five optically selected QSO2s at redshift z ∼ 0.1 obtained with the Medium Resolution Spectrometer module of the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) aboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). These QSO2s belong to the Quasar Feedback (QSOFEED) sample, and they have bolometric luminosities of log L bol = 45.5 to 46.0 erg s −1 , global starAdvertised on
Type 2 quasars (QSO2s) are active galactic nuclei (AGN) seen through a significant amount of dust and gas that obscures the central supermassive black hole and the broad-line region. Here, we present new mid-infrared spectra of the central kiloparsec of five optically selected QSO2s at redshift z ∼ 0.1 obtained with the Medium Resolution Spectrometer module of the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) aboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). These QSO2s belong to the Quasar Feedback (QSOFEED) sample, and they have bolometric luminosities of log L bol = 45.5 to 46.0 erg s −1 , global starAdvertised on -
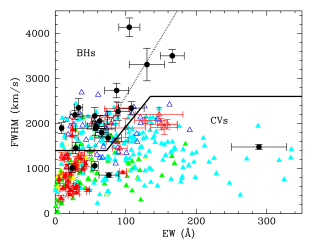 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
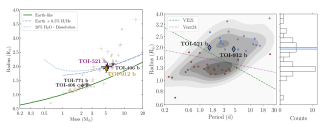 Sub-Neptunes - planets larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune - are the most common type of planet in our Galaxy, yet they are entirely absent from our own Solar System. This absence makes them a major focus for astronomers seeking to understand planetary formation and evolution. We recently conducted an international study, as part of the THIRSTEE project, to characterize two such planets orbiting very similar small, cool stars known as M dwarfs: TOI-521 and TOI-912 . THIRSTEE is an observational-based program that aims to shed light on the sub-Neptune population by providing anAdvertised on
Sub-Neptunes - planets larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune - are the most common type of planet in our Galaxy, yet they are entirely absent from our own Solar System. This absence makes them a major focus for astronomers seeking to understand planetary formation and evolution. We recently conducted an international study, as part of the THIRSTEE project, to characterize two such planets orbiting very similar small, cool stars known as M dwarfs: TOI-521 and TOI-912 . THIRSTEE is an observational-based program that aims to shed light on the sub-Neptune population by providing anAdvertised on
