We use deep Hubble Space Telescope Advanced Camera for Surveys/High Resolution Channel observations of a field within M32 (F1) and an M31 background field (F2) to determine the star formation history (SFH) of M32 from its resolved stellar population. We find that 2-5 Gyr old stars contribute ~40% ± 17% of M32's mass, while ~55% ± 21% of M32's mass comes from stars older than 5 Gyr. The SFH additionally indicates the presence of young (<2 Gyr old), metal-poor ([M/H] ~ –0.7) stars, suggesting that blue straggler stars contribute ~2% of the mass at F1; the remaining ~3% of the mass is in young metal-rich stars. The inferred SFH of the M31 background field F2 reveals that the majority of its stars are old, with ~95% of its mass already acquired 5-14 Gyr ago. It is composed of two dominant populations; ~30% ± 7.5% of its mass is in a 5-8 Gyr old population, and ~65% ± 9% of the mass is in an 8-14 Gyr old population. Our results suggest that the inner disk and spheroid populations of M31 are indistinguishable from those of the outer disk and spheroid. Assuming the mean age of M31's disk at F2 (~1 disk scale length) to be ~5-9 Gyr, our results agree with an inside-out disk formation scenario for M31's disk.
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
 WISEA J181006.18-101000.5 (WISE1810) is the nearest metal-poor ultracool dwarf to the Sun. It has a low effective temperature and has been classified as an extreme early-T subdwarf. However, methane--the characteristic molecule of the spectral class T--was not detected in the previous low-resolution spectrum. Constraining the metallicity--the abundance of elements heavier than helium-- of these cold objects has been a challenge. Using the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias, the largest optical-infrared telescope in the world, we collected a high-quality near-infrared intermediate-resolutionAdvertised on
WISEA J181006.18-101000.5 (WISE1810) is the nearest metal-poor ultracool dwarf to the Sun. It has a low effective temperature and has been classified as an extreme early-T subdwarf. However, methane--the characteristic molecule of the spectral class T--was not detected in the previous low-resolution spectrum. Constraining the metallicity--the abundance of elements heavier than helium-- of these cold objects has been a challenge. Using the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias, the largest optical-infrared telescope in the world, we collected a high-quality near-infrared intermediate-resolutionAdvertised on -
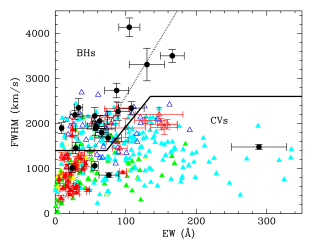 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
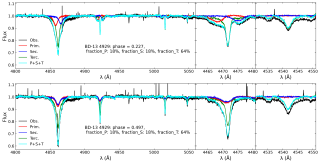 The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
