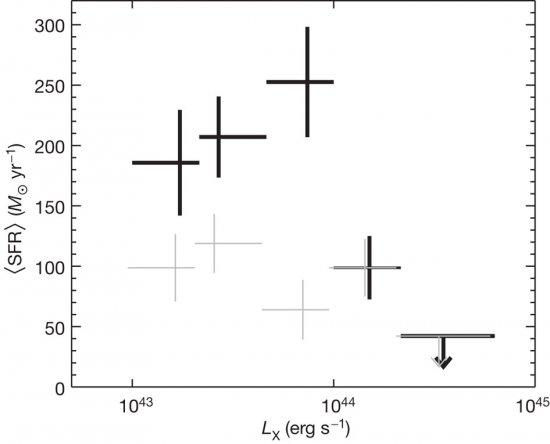
The old, red stars that constitute the bulges of galaxies, and the massive black holes at their centres, are the relics of a period in cosmic history when galaxies formed stars at remarkable rates and active galactic nuclei (AGN) shone brightly as a result of accretion onto black holes. It is widely suspected, but unproved, that the tight correlation between the mass of the black hole and the mass of the stellar bulge results from the AGN quenching the surrounding star formation as it approaches its peak luminosity. X-rays trace emission from AGN unambiguously, whereas powerful star-forming galaxies are usually dust-obscured and are brightest at infrared and submillimetre wavelengths. Here we report submillimetre and X-ray observations that show that rapid star formation was common in the host galaxies of AGN when the Universe was 2-6 billion years old, but that the most vigorous star formation is not observed around black holes above an X-ray luminosity of 1044 ergs per second. This suppression of star formation in the host galaxy of a powerful AGN is a key prediction of models in which the AGN drives an outflow, expelling the interstellar medium of its host and transforming the galaxy's properties in a brief period of cosmic time.
Average star formation rates, (SFR), derived from averaged far-infrared luminosities of 1<z<3 AGNs, as a function of suLX.
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
 In the standard Lambda cold dark matter (Lambda-CDM) cosmology, galaxies grow by gradually accreting material and through mergers with other galaxies. This scenario successfully explains many large-scale cosmic structures, yet it struggles to account for the existence of numerous massive spiral galaxies in the local Universe that lack a prominent central bulge, pure disc systems, in the local Universe. Understanding how these galaxies form and survive is also essential for placing our own Galaxy, the Milky Way, into context, as it also hosts a low-mass bulge. In this study, we analyse 22Advertised on
In the standard Lambda cold dark matter (Lambda-CDM) cosmology, galaxies grow by gradually accreting material and through mergers with other galaxies. This scenario successfully explains many large-scale cosmic structures, yet it struggles to account for the existence of numerous massive spiral galaxies in the local Universe that lack a prominent central bulge, pure disc systems, in the local Universe. Understanding how these galaxies form and survive is also essential for placing our own Galaxy, the Milky Way, into context, as it also hosts a low-mass bulge. In this study, we analyse 22Advertised on -
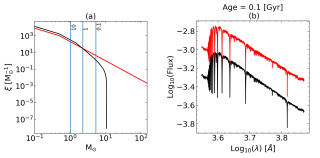 We present, for the first time, model spectra of single-age, single-metallicity stellar populations computed with the E-MILES evolutionary synthesis code incorporating an environment-dependent, variable galaxy-wide initial mass function (gwIMF). This gwIMF, calculated using the GalIMF code, is rooted in the integrated galactic initial mass function (IGIMF) theory, which predicts IMF variations as a function of the star formation rate and the metallicity. By coupling these two codes, we generated a comprehensive library of single-burst stellar population spectra uniquely sensitive to gwIMFAdvertised on
We present, for the first time, model spectra of single-age, single-metallicity stellar populations computed with the E-MILES evolutionary synthesis code incorporating an environment-dependent, variable galaxy-wide initial mass function (gwIMF). This gwIMF, calculated using the GalIMF code, is rooted in the integrated galactic initial mass function (IGIMF) theory, which predicts IMF variations as a function of the star formation rate and the metallicity. By coupling these two codes, we generated a comprehensive library of single-burst stellar population spectra uniquely sensitive to gwIMFAdvertised on -
 In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on
In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on