Bibcode
Duivenvoorden, S.; Oliver, S.; Béthermin, M.; Clements, D. L.; De Zotti, G.; Efstathiou, A.; Farrah, D.; Hurley, P. D.; Ivison, R. J.; Lagache, G.; Scott, D.; Shirley, R.; Wang, L.; Zemcov, M.
Bibliographical reference
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Advertised on:
1
2020
Citations
12
Refereed citations
9
Description
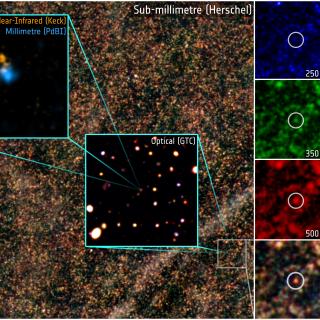
The cosmic infrared background (CIB) provides a fundamental observational constraint on the star formation history of galaxies over cosmic history. We estimate the contribution to the CIB from catalogued galaxies in the COSMOS field by using a novel map fitting technique on the Herschel SPIRE maps. Prior galaxy positions are obtained using detections over a large range in wavelengths in the Ks-3 GHz range. Our method simultaneously fits the galaxies, the system foreground, and the leakage of flux from galaxies located in masked areas and corrects for an 'overfitting' effect not previously accounted for in stacking methods. We explore the contribution to the CIB as a function of galaxy survey wavelength and depth. We find high contributions to the CIB with the deep r (mAB ≤ 26.5), Ks (mAB ≤ 24.0), and 3.6 μm (mAB ≤ 25.5) catalogues. We combine these three deep catalogues and find a total CIB contributions of 10.5 ± 1.6, 6.7 ± 1.5, and 3.1 ± 0.7 nWm-2 sr-1 at 250, 350, and 500 μm, respectively. Our CIB estimates are consistent with recent phenomenological models, prior based SPIRE number counts and with (though more precise than) the diffuse total measured by FIRAS. Our results raise the interesting prospect that the CIB contribution at λ ≤ 500 μm from known galaxies has converged. Future large-area surveys like those with the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope are therefore likely to resolve a substantial fraction of the population responsible for the CIB at 250 μm ≤ λ ≤ 500 μm.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon