Bibcode
Gavazzi, R.; Cooray, A.; Conley, A.; Aguirre, J. E.; Amblard, A.; Auld, R.; Beelen, A.; Blain, A.; Blundell, R.; Bock, J.; Bradford, C. M.; Bridge, C.; Brisbin, D.; Burgarella, D.; Chanial, P.; Chapin, E.; Christopher, N.; Clements, D. L.; Cox, P.; Djorgovski, S. G.; Dowell, C. D.; Eales, S.; Earle, L.; Ellsworth-Bowers, T. P.; Farrah, D.; Franceschini, A.; Fu, H.; Glenn, J.; González Solares, E. A.; Griffin, M.; Gurwell, M. A.; Halpern, M.; Ibar, E.; Ivison, R. J.; Jarvis, M.; Kamenetzky, J.; Kim, S.; Krips, M.; Levenson, L.; Lupu, R.; Mahabal, A.; Maloney, P. D.; Maraston, C.; Marchetti, L.; Marsden, G.; Matsuhara, H.; Mortier, A. M. J.; Murphy, E.; Naylor, B. J.; Neri, R.; Nguyen, H. T.; Oliver, S. J.; Omont, A.; Page, M. J.; Papageorgiou, A.; Pearson, C. P.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Pohlen, M.; Rangwala, N.; Rawlings, J. I.; Raymond, G.; Riechers, D.; Rodighiero, G.; Roseboom, I. G.; Rowan-Robinson, M.; Schulz, B.; Scott, Douglas; Scott, K. S.; Serra, P.; Seymour, N.; Shupe, D. L.; Smith, A. J.; Symeonidis, M.; Tugwell, K. E.; Vaccari, M.; Valiante, E.; Valtchanov, I.; Verma, A.; Vieira, J. D.; Vigroux, L.; Wang, L.; Wardlow, J.; Wiebe, D.; Wright, G.; Xu, C. K.; Zeimann, G.; Zemcov, M.; Zmuidzinas, J.
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 738, Issue 2, article id. 125 (2011).
Advertised on:
9
2011
Journal
Citations
31
Refereed citations
28
Description
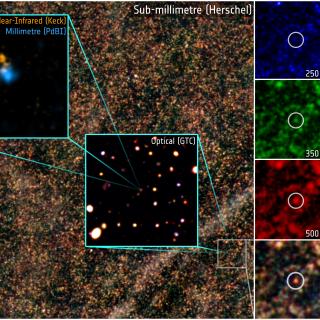
We present the results of a gravitational lensing analysis of the bright
z s = 2.957 submillimeter galaxy (SMG) HERMES found in the
Herschel/SPIRE science demonstration phase data from the Herschel
Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) project. The high-resolution
imaging available in optical and near-IR channels, along with CO
emission obtained with the Plateau de Bure Interferometer, allows us to
precisely estimate the intrinsic source extension and hence estimate the
total lensing magnification to be μ = 10.9 ± 0.7. We measure
the half-light radius R eff of the source in the rest-frame
near-UV and V bands that characterize the unobscured light coming from
stars and find R eff, * = [2.0 ± 0.1] kpc, in good
agreement with recent studies on the SMG population. This lens model is
also used to estimate the size of the gas distribution (R eff,
gas = [1.1 ± 0.5] kpc) by mapping back in the source plane
the CO (J = 5 → 4) transition line emission. The lens modeling
yields a relatively large Einstein radius R Ein = 4farcs10
± 0farcs02, corresponding to a deflector velocity dispersion of
[483 ± 16] km s-1. This shows that HERMES is lensed by
a galaxy group-size dark matter halo at redshift z l ~ 0.6.
The projected dark matter contribution largely dominates the mass budget
within the Einstein radius with f dm(< R Ein) ~
80%. This fraction reduces to f dm(< R eff, G1
~= 4.5 kpc) ~ 47% within the effective radius of the main deflecting
galaxy of stellar mass M *, G1 = [8.5 ± 1.6] ×
1011 M sun. At this smaller scale the dark matter
fraction is consistent with results already found for massive lensing
ellipticals at z ~ 0.2 from the Sloan Lens ACS Survey.
Some of the data presented herein were obtained at the W. M. Keck
Observatory which is operated as a scientific partnership among the
California Institute of Technology, the University of California, and
the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The Observatory was
made possible by the generous financial support of the W. M. Keck
Foundation.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon