Turbulence is a particular motion of fluids where the kinetic energy breaks the laminar flow. Optical turbulence refers to the effects that this motion has on light. The optical turbulence in the atmosphere is caused by the fluctuations in the index of refraction of the air, which depends on the wind and temperature inhomogeneities. Finally, the vertical distribution of turbulence is the knowledge of how the layers of turbulence are organized in the atmosphere (up to ~20 km of height).
The optical turbulence is the responsible of the image degradation in Astronomy from Earth. Knowing the amount and distribution of turbulence is key for determining the observing conditions, the quality of the observations, the design of telescopes and instrumentation, and the performance of high resolution techniques, such as the adaptive optics.
All the parameters relevant for the image quality (seeing, isoplanatic angle and coherence time) can be obtained from the optical turbulence profile, given by a statistical parameter called the refractive-index structure constant of the turbulence, Cn2(h), where h is the altitude.
Different techniques may be used to retrieve the vertical profile of optical turbulence. From direct measurements obtained with radiosounding ballooons to remote sensing methods such as SLODAR, MASS or gSCIDAR, one of the most reliable and complete techniques to retrieve Cn2(h). On the other hand gSCIDAR requires a relatively large telescope (>1 m), which limits its usability as a routine operational monitor.
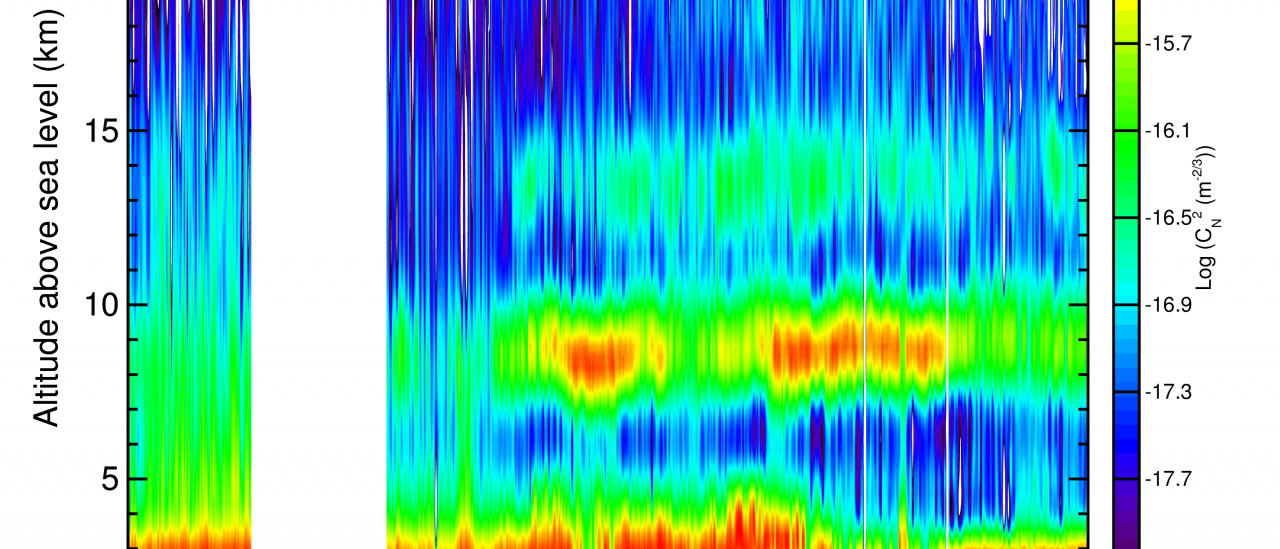
Two gSCIDAR instruments were routinely operated at ORM and OT for several years. A complete summary of the results at both Observatories, covering more than 200 nights at each, are in two studies by Garcia-Lorenzo et al (2011) at the ORM and the OT. Similar average profiles are found for ORM and OT, as a consequence of the mesoscale conditions governing the atmosphere of both sites (Castro-Almazan et al, 2009). The following figure shows the monthly behaviour of the turbulence over the ORM from a dataset of 197,035 individual profiles obtained with gSCIDAR in 211 nights from 2004 to 2009. Note that the Cn2(h) is given in a logarithmic scale.
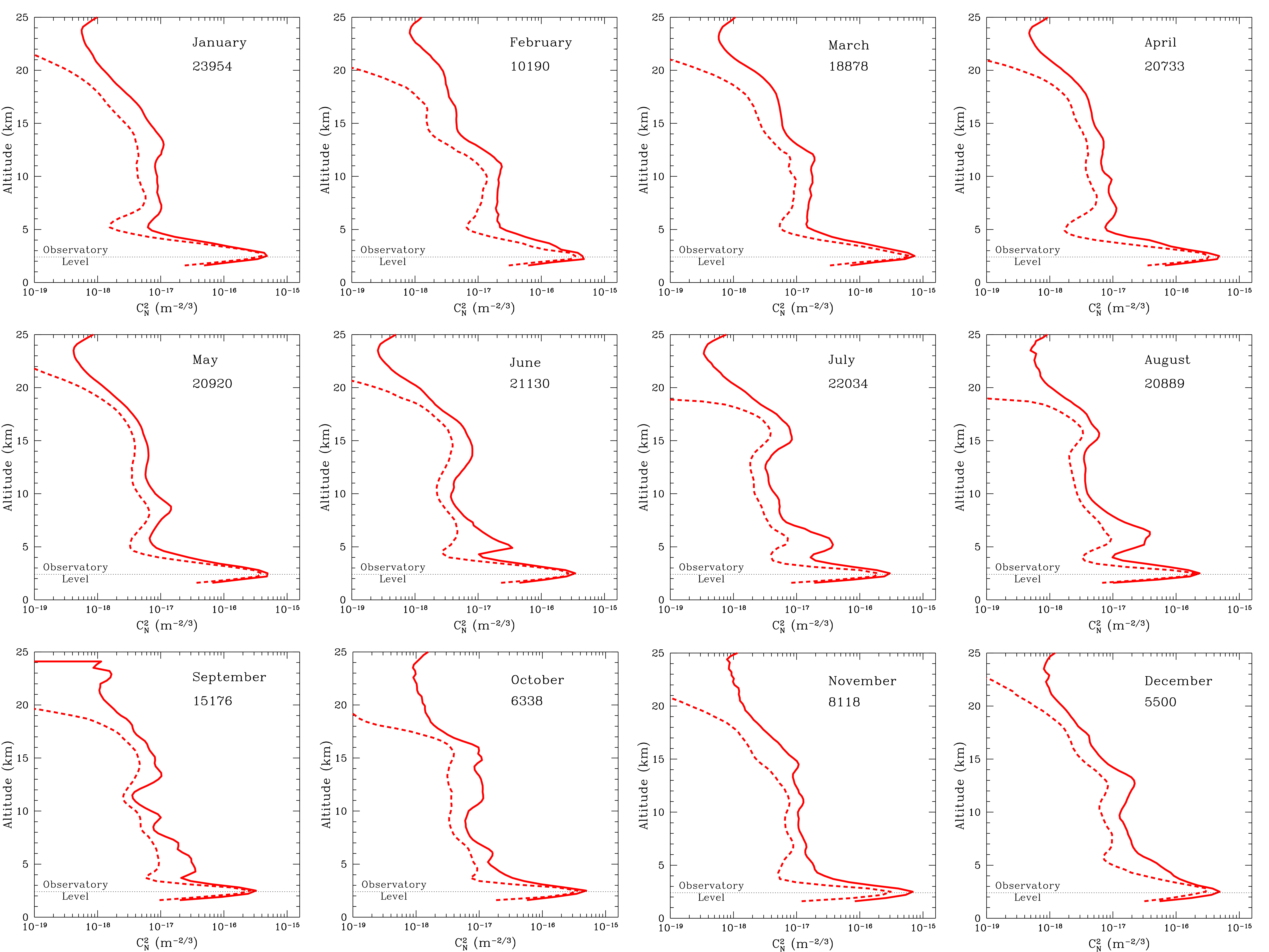
Most of the turbulence at ORM is concentrated in the first kilometer (Boundary Layer). Secondary layers may be found between ≈6 km (above sea level) and ≈16 km in summer months, associated with the subtropical jet stream and the Troposphere top.Most of the turbulence at ORM is concentrated in the Boundary Layer (first kilometer above ground). Secondary layers may be found between ≈6 km (above sea level) and ≈16 km in summer months, associated with the subtropical jet stream and the Troposphere top.
Boundary Layer
The contribution of the boundary layer to the total turbulence at the ORM and OT is around 70%. This value has been confirmed by measurements with gSCIDAR (Garcia-Lorenzo 2011; ORM and OT ), MASS (Vazquez-Ramio et al, 2012) or the early work with radiosounding balloons by Vernin et al (1992). This ratio (higher than measured at other very good sites) improves the potential for compensation with multiconjugated adaptive optics (MCAO).
Surface Layer
Most of the Surface Layer turbulence is concentrated in the first 6 m. This was the result of a set of direct measurements using microthermal probes in a meteorological mast with sensors at 6, 9 and 12 m (Vernin et al, 1994).
gSCIDAR database
The full gSCIDAR database at both observatories is freely available only for non-profit research under request. The full database includes 200 000 profiles from more than 200 nights at ORM and 100 000 profiles from 150 nights at OT.