Bibcode
Ascaso, B.; Aguerri, J. A. L.; Varela, J.; Cava, A.; Bettoni, D.; Moles, M.; D'Onofrio, M.
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 726, Issue 2, article id. 69 (2011).
Advertised on:
1
2011
Journal
Citations
52
Refereed citations
49
Description
We present results on the evolution of the structural parameters of two
samples of brightest cluster galaxies (BCGs) in the last 6 Gyr. The
nearby sample of BCGs consists of 69 galaxies from the WINGS survey
spanning a redshift range of 0.04 < z < 0.07. The
intermediate-redshift (0.3 < z < 0.6) sample is formed by 20 BCGs
extracted from the Hubble Space Telescope archive. Both samples have
similar spatial resolution and their host clusters have similar X-ray
luminosities. We report an increase in the size of the BCGs from
intermediate to local redshift. However, we do not detect any variation
in the Sérsic shape parameter in both samples. These results
prove to be robust since the observed tendencies are model independent.
We also obtain significant correlations between some of the BCG
parameters and the main properties of the host clusters. More luminous,
larger, and centrally located BCGs are located in more massive and
dominant galaxy clusters. These facts indicate that the host galaxy
cluster has played an important role in the formation of their BCGs. We
discuss the possible mechanisms that can explain the observed evolution
of the structural parameters of the BCGs. We conclude that the main
mechanisms that can explain the increase in size and the non-evolution
in the Sérsic shape parameter of the BCGs in the last 6 Gyr are
feedback processes. This result disagrees with semi-analytical
simulation results supporting the idea that merging processes are the
main mechanism responsible for the evolution of the BCGs up until the
present epoch.
Related projects
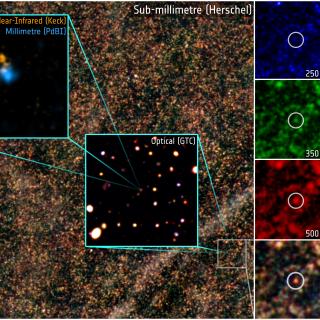
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon

Galaxy Evolution in Clusters of Galaxies
Galaxies in the universe can be located in different environments, some of them are isolated or in low density regions and they are usually called field galaxies. The others can be located in galaxy associations, going from loose groups to clusters or even superclusters of galaxies. One of the foremost challenges of the modern Astrophysics is to
Jairo
Méndez Abreu