Bibcode
Planck Collaboration; Aghanim, N.; Armitage-Caplan, C.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A. J.; Barreiro, R. B.; Battaner, E.; Benabed, K.; Benoît, A.; Benoit-Lévy, A.; Bernard, J.-P.; Bersanelli, M.; Bielewicz, P.; Bobin, J.; Bock, J. J.; Bonaldi, A.; Bonavera, L.; Bond, J. R.; Borrill, J.; Bouchet, F. R.; Bridges, M.; Bucher, M.; Burigana, C.; Butler, R. C.; Cardoso, J.-F.; Catalano, A.; Chamballu, A.; Chiang, L.-Y.; Christensen, P. R.; Church, S.; Colombi, S.; Colombo, L. P. L.; Crill, B. P.; Cruz, M.; Curto, A.; Cuttaia, F.; Danese, L.; Davies, R. D.; Davis, R. J.; de Bernardis, P.; de Rosa, A.; de Zotti, G.; Delabrouille, J.; Dick, J.; Dickinson, C.; Diego, J. M.; Dole, H.; Donzelli, S.; Doré, O.; Douspis, M.; Dupac, X.; Efstathiou, G.; Enßlin, T. A.; Eriksen, H. K.; Finelli, F.; Forni, O.; Frailis, M.; Franceschi, E.; Gaier, T. C.; Galeotta, S.; Ganga, K.; Giard, M.; Giraud-Héraud, Y.; Gjerløw, E.; González-Nuevo, J.; Górski, K. M.; Gratton, S.; Gregorio, A.; Gruppuso, A.; Hansen, F. K.; Hanson, D.; Harrison, D.; Henrot-Versillé, S.; Hernández-Monteagudo, C.; Herranz, D.; Hildebrandt, S. R.; Hivon, E.; Hobson, M.; Holmes, W. A.; Hornstrup, A.; Hovest, W.; Huffenberger, K. M.; Jaffe, A. H.; Jaffe, T. R.; Jewell, J.; Jones, W. C.; Juvela, M.; Kangaslahti, P.; Keihänen, E.; Keskitalo, R.; Kiiveri, K.; Kisner, T. S.; Knoche, J.; Knox, L.; Kunz, M.; Kurki-Suonio, H. et al.
Bibliographical reference
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 571, id.A3, 23 pp.
Advertised on:
11
2014
Journal
Citations
53
Refereed citations
51
Description
We present the current estimate of instrumental and systematic effect
uncertainties for the Planck-Low Frequency Instrument relevant to the
first release of the Planck cosmological results. We give an overview of
the main effects and of the tools and methods applied to assess
residuals in maps and power spectra. We also present an overall budget
of known systematic effect uncertainties, which are dominated by
sidelobe straylight pick-up and imperfect calibration. However, even
these two effects are at least two orders of magnitude weaker than the
cosmic microwave background fluctuations as measured in terms of the
angular temperature power spectrum. A residual signal above the noise
level is present in the multipole range ℓ < 20, most notably at
30 GHz, and is probably caused by residual Galactic straylight
contamination. Current analysis aims to further reduce the level of
spurious signals in the data and to improve the systematic effects
modelling, in particular with respect to straylight and calibration
uncertainties.
Related projects
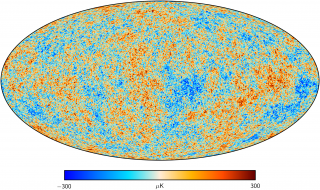
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López