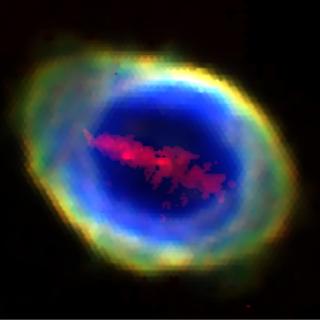
An international scientific team, involving the University of La Laguna (ULL) and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has identified the cause of an unusually long dimming of a distant star . The phenomenon is explained by the passage of a substellar object with a giant ring system, similar to a ‘cosmic saucer’, in front of the host star. The star, named ASASSN-24fw, is located in the Monoceros constellation at about 3,000 light-years away from Earth. The star faded steadily for more than nine months between late 2024 and mid-2025 to about 97% dark before returning to its normal
Advertised on