Bibcode
Martínez-González, M. J.; Manso-Sainz, R.; Asensio-Ramos, A.; Hijano, E.
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 755, Issue 2, article id. 175 (2012).
Advertised on:
8
2012
Journal
Citations
36
Refereed citations
29
Description
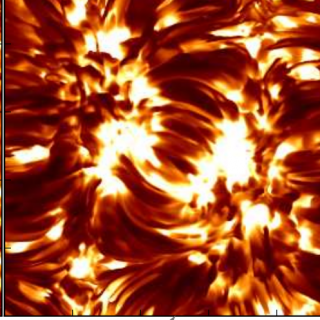
We analyze two regions of the quiet Sun (35.6 × 35.6
Mm2) observed at high spatial resolution (lsim100 km) in
polarized light by the IMaX spectropolarimeter on board the SUNRISE
balloon. We identify 497 small-scale (~400 km) magnetic loops, appearing
at an effective rate of 0.25 loop h -1
arcsec-2 further, we argue that this number and rate
are underestimated by ~30%. However, we find that these small dipoles do
not appear uniformly on the solar surface: their spatial distribution is
rather filamentary and clumpy, creating dead calm areas, characterized
by a very low magnetic signal and a lack of organized loop-like
structures at the detection level of our instruments, which cannot be
explained as just statistical fluctuations of a Poisson spatial process.
We argue that this is an intrinsic characteristic of the mechanism that
generates the magnetic fields in the very quiet Sun. The spatio-temporal
coherences and the clumpy structure of the phenomenon suggest a
recurrent, intermittent mechanism for the generation of magnetic fields
in the quietest areas of the Sun.
Related projects

Solar and Stellar Magnetism
Magnetic fields are at the base of star formation and stellar structure and evolution. When stars are born, magnetic fields brake the rotation during the collapse of the mollecular cloud. In the end of the life of a star, magnetic fields can play a key role in the form of the strong winds that lead to the last stages of stellar evolution. During
Carlos Cristo
Quintero Noda
Magnetism, Polarization and Radiative Transfer in Astrophysics
Magnetic fields pervade all astrophysical plasmas and govern most of the variability in the Universe at intermediate time scales. They are present in stars across the whole Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, in galaxies, and even perhaps in the intergalactic medium. Polarized light provides the most reliable source of information at our disposal for the
Ernest
Alsina Ballester