Related grants:
General
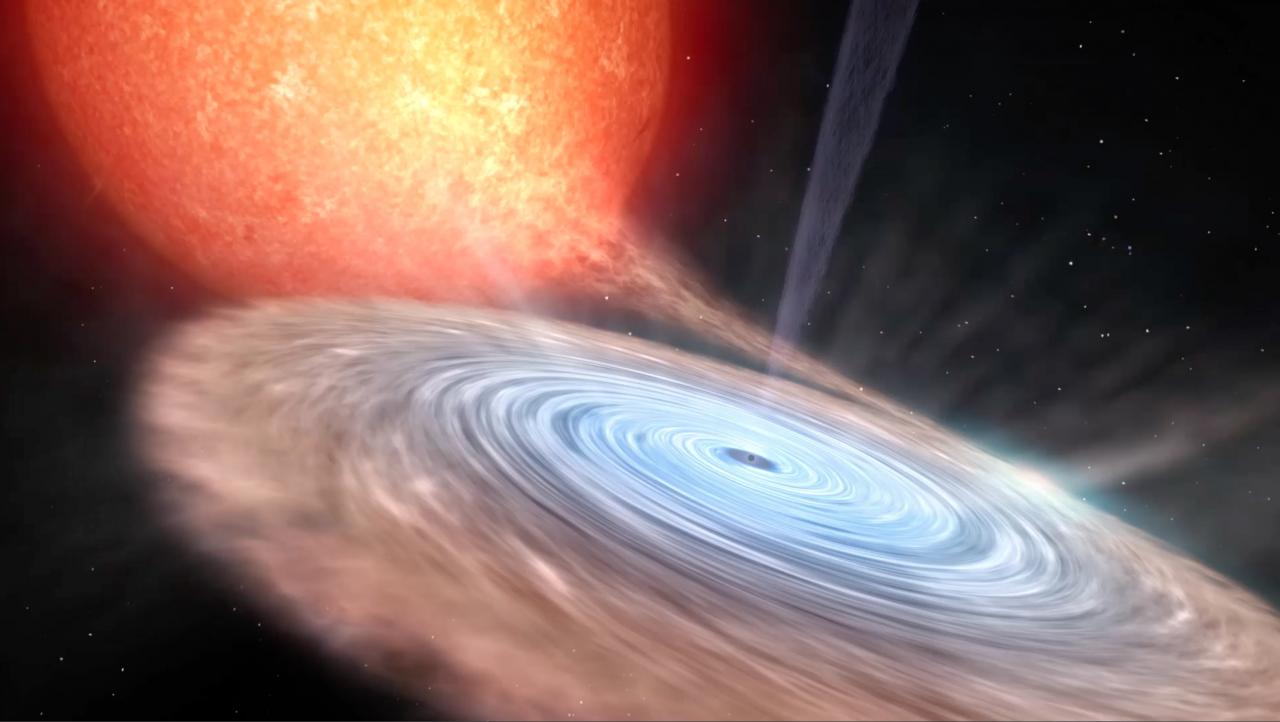
Accreting black-holes and neutron stars in X-ray binaries provide an ideal laboratory for exploring the physics of compact objects, yielding not only confirmation of the existence of stellar mass black holes via dynamical mass measurements, but also the best opportunity for probing high-gravity environments and the physics of accretion; the most efficient form of energy production known. The latter is an essential physical process to understand the universe, playing a crucial role in galactic and extra-galactic astronomy.
This project has the following scientific goals:
- X-ray binaries offer the opportunity to study accretion as its best, since their relevant changes occur on convenient time-scales for human beings. This project focuses on the universal relation between black-hole accretion and ejection processes in the form of collimated jets and wide-angle winds. We will focus on the general properties and astrophysical impact of the cold optical accretion disc wind that our group has discovered. We want to understand how frequent these winds are, which is their impact in the black-hole accretion process, and what is their relation with jets and hot X-ray winds. Likewise, we carry out very detailed X-ray spectral studies on the different accretion states and geometries and their evolution with luminosity.
- We want to define the mass distribution of black-holes and neutron stars. Thus, we continue our contribution to one of the fundamental experiments in modern astrophysics by measuring dynamical masses in X-ray binaries. We expect to significantly improve the observed mass distribution of compact objects. This will allow testing models of supernovae explosions and close binary evolution as well as setting constraints on the equation of state of nuclear matter. We will measure masses in newly discovered or known transient X-ray binaries. In addition, we will also search for the large number of dormant X-ray binaries expected in the Galaxy and suitable for dynamical studies.
- To study the structure of accretion discs in different energy bands (optical-X rays). The high energy spectral distribution and time variability during outburst is important to constrain the eruption models and accretion disc properties (e.g. radius of advective disc) as well as to constrain the contribution of the jet to the optical and infrared emission of the system.
see group web page: https://research.iac.es/proyecto/compactos/pages/en/introduction.php
Members
Results
- Our team has led the multi-wavelength study of the two 2015 outbursts of the Black-hole transient V404 Cyg. In 2018, we published a global paper which include all the spectroscopy taken during the 1989 and 2015 campaigns.
- We have presented solid evidence for the presence of very similar wind to that found in V404 Cyg in another black hole transient, V4641 Sgr.
- We published the final paper as well as a pilot study on a novel method developed by the group. It aims at discovering and measuring masses of black hole transient in quiescence. This method has the potential of increasing the known population of these systems by a factor of three.
- We measured the mass of the neutron star in PSR J2215+5135 and found it is one of the heaviest known to date.
- We presented the first detailed study on the ultra-compact system SLX 1737-282.