Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
Este grupo desarrolla varios proyectos extragalácticos en diferentes rangos del espectro electromagnético utilizando satélites y telescopios en tierra para estudiar la evolución cosmológica de las galaxias y el origen de la actividad nuclear en galaxias activas. En el aspecto instrumental, el grupo forma parte del consorcio internacional que ha construido el instrumento SPIRE del Observatorio Espacial Herschel y del consorcio europeo que desarrolla el instrumento SAFARI para el telescopio espacial infrarrojo SPICA de las agencias espaciales ESA y JAXA.
Los proyectos principales en 2018 han sido:
a) Galaxias y cuásares distantes con emisión en el infrarrojo lejano descubiertas con el Observatorio Espacial Herschel en los "Key Projects" HerMES y Herschel-ATLAS.
b) Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV: galaxias del proyecto BELLS GALLERY y galaxias Lyman alpha muy luminosas
c) Participación en el desarrollo del instrumento SAFARI, una de las contribuciones europeas al telescopio espacial infrarrojo SPICA.
d) Descubrimiento de la estrella individual más distante conocida, en uno de los campos del proyecto "HST Frontier Fields"
e) Búsqueda de supernovas en galaxias distantes amplificadas por lentes gravitacionales.
f) Varios estudios con GTC de sistemas de absorción en la línea de visión a cuásares rojos.
Miembros
Resultados
- Marques-Chaves et al. (2018) presentan un estudio detallado de la galaxia submm HLock01 a z = 2.9574, una de las fuentes más brillantes magnificadas por una lente gravitacional descubiertas en el "Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey".
- Rigopoulou et al. (2018) derivan la metalicidad de la fase gaseosa de la galaxia submm HLSW-01 utilizando observaciones espectroscópicas de líneas de estructura fina con Herschel. Encuentran que la metalicidad de galaxias submm luminosas es de tipo solar y que siguen la relación masa-metalicidad esperada para galaxias a z ∼ 3.
- Cornachione et al. (2018) presentan un estudio morfológico de 17 galaxias emisoras Lyman alpha magnificadas por lentes gravitacionales de la muestra BELLS GALLERY. El análisis combina el efecto de magnificación de las lentes fuertes galaxia-galaxia con la alta resolución angular del telescopio espacial Hubble para conseguir una resolución espacial de ~80 pc.
- Oteo et al. (2018) reportan la identificación de un protocúmulo de galaxias extremo en el universo temprano cuyo núcleo (denominado Núcleo Rojo Distante por su color muy rojo en las bandas de Herschel SPIRE) está formado por al menos 10 galaxias polvorientas con formación estelar, confirmadas espectroscópicamente a z = 4.002 con ALMA y ATCA.
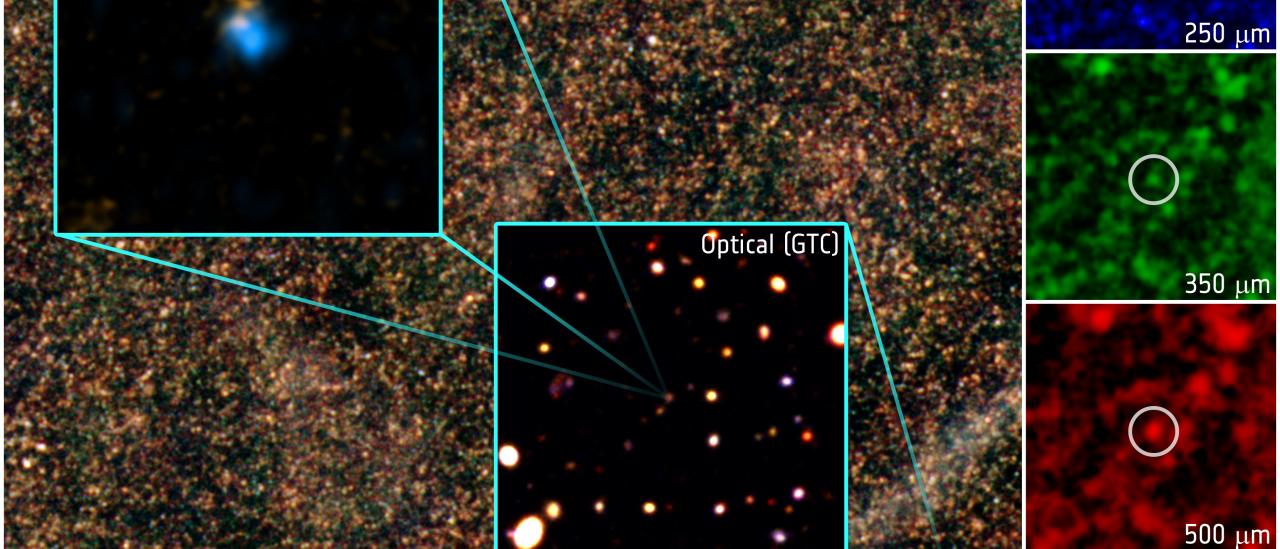
- Kelly et al. (2018) reportan el descubrimiento de una estrella individual, Icarus, a un desplazamiento al rojo de 1.49, magnificada más de 2000 veces por el efecto de lente gravitacional del cúmulo de galaxias MACS J1149+222. Icarus está localizada en una galaxia espiral muy alejada de la tierra, su luz ha tardado 9000 millones de años en llegar a la tierra.
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
-
HerMES: SPIRE galaxy number counts at 250, 350, and 500 μm
Emission at far-infrared wavelengths makes up a significant fraction of the total light detected from galaxies over the age of Universe. Herschel provides an opportunity for studying galaxies at the peak wavelength of their emission. Our aim is to provide a benchmark for models of galaxy population evolution and to test pre-existing models of
Oliver, S. J. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
HerMES: Halo occupation number and bias properties of dusty galaxies from angular clustering measurements
We measure the angular correlation function, w(θ), from 0.5 to 30 arcmin of detected sources in two wide fields of the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES). Our measurements are consistent with the expected clustering shape from a population of sources that trace the dark matter density field, including non-linear clustering at
Cooray, A. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
HerMES: Far infrared properties of known AGN in the HerMES fields
Nuclear and starburst activity are known to often occur concomitantly. Herschel-SPIRE provides sampling of the far-infrared (FIR) spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of type 1 and type 2 AGN, allowing for the separation between the hot dust (torus) and cold dust (starburst) emission. We study large samples of spectroscopically confirmed type 1 and
Hatziminaoglou, E. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
Galaxy Counts at 24 μm in the SWIRE Fields
This paper presents galaxy source counts at 24 μm in the six Spitzer Wide-field InfraRed Extragalactic (SWIRE) fields. The source counts are compared to counts in other fields, and to model predictions that have been updated since the launch of Spitzer. This analysis confirms a very steep rise in the Euclidean-normalized differential number counts
Shupe, David L. et al.Fecha de publicación:
32008 -
First results from HerMES on the evolution of the submillimetre luminosity function
We have carried out two extremely deep surveys with SPIRE, one of the two cameras on Herschel, at 250 μm, close to the peak of the far-infrared background. We have used the results to investigate the evolution of the rest-frame 250-μm luminosity function out to z = 2. We find evidence for strong evolution out to z ≃ 1 but evidence for at most weak
Eales, S. A. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
Wide-field optical imaging on ELAIS N1, ELAIS N2, First Look Survey and Lockman Hole: observations and source catalogues
We present u-, g-, r-, i- and z-band optical images and associated catalogues taken primarily with the Isaac Newton Telescope Wide Field Camera on the European Large Area ISO Survey (ELAIS) N1 and N2, First Look Survey and Lockman Hole fields comprising a total of 1000 h of integration time over 80 deg2 and approximately 4.3 million objects. In
González-Solares, E. A. et al.Fecha de publicación:
92011 -
The suppression of star formation by powerful active galactic nuclei
The old, red stars that constitute the bulges of galaxies, and the massive black holes at their centres, are the relics of a period in cosmic history when galaxies formed stars at remarkable rates and active galactic nuclei (AGN) shone brightly as a result of accretion onto black holes. It is widely suspected, but unproved, that the tight
Page, M. J. et al.Fecha de publicación:
52012 -
The Spitzer Extragalactic Representative Volume Survey (SERVS): Survey Definition and Goals
We present the Spitzer Extragalactic Representative Volume Survey (SERVS), an 18 deg2 medium-deep survey at 3.6 and 4.5 μm with the postcryogenic Spitzer Space Telescope to ≈2 mJy (AB=23.1) depth of five highly observed astronomical fields (ELAIS-N1, ELAIS-S1, Lockman Hole, Chandra Deep Field South, and XMM-LSS). SERVS is designed to enable the
Mauduit, J.-C. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72012 -
The Herschel Space Observatory view of dust in M81
We use Herschel Space Observatory data to place observational constraints on the peak and Rayleigh-Jeans slope of dust emission observed at 70-500 μm in the nearby spiral galaxy M81. We find that the ratios of wave bands between 160 and 500 μm are primarily dependent on radius but that the ratio of 70 to 160 μm emission shows no clear dependence on
Bendo, G. J. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey: SPIRE-mm photometric redshifts
We investigate the potential of submm-mm and submm-mm-radio photometric redshifts using a sample of mm-selected sources as seen at 250, 350 and 500μm by the SPIRE instrument on Herschel. From a sample of 63 previously identified mm sources with reliable radio identifications in the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey North and Lockman Hole
Roseboom, I. G. et al.Fecha de publicación:
22012 -
The Herschel Multi-Tiered Extragalactic Survey: source extraction and cross-identifications in confusion-dominated SPIRE images
We present the cross-identification and source photometry techniques used to process Herschel SPIRE imaging taken as part of the Herschel Multi-Tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES). Cross-identifications are performed in map-space so as to minimize source-blending effects. We make use of a combination of linear inversion and model selection
Roseboom, I. G. et al.Fecha de publicación:
112010 -
The dust morphology of the elliptical Galaxy M 86 with SPIRE
We present Herschel-SPIRE observations at 250-500 μm of the giant elliptical galaxy M 86 and examine the distribution of the resolved cold dust emission and its relation with other galactic tracers. The SPIRE images reveal three dust components: emission from the central region; a dust lane extending north-south; and a bright emission feature 10
Gomez, H. L. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
The Deep SPIRE HerMES Survey: spectral energy distributions and their astrophysical indications at high redshift
The Spectral and Photometric Imaging Receiver on-board Herschel has been carrying out deep extragalactic surveys, one of the aims of which is to establish spectral energy distributions of individual galaxies spanning the infrared/submillimetre (IR/SMM) wavelength region. We report observations of the IR/SMM emission from the Lockman North field and
Brisbin, D. et al.Fecha de publicación:
112010 -
The central region of spiral galaxies as seen by Herschel. M 81, M 99, and M 100
With appropriate spatial resolution, images of spiral galaxies in thermal infrared (~10 μm and beyond) often reveal a bright central component, distinct from the stellar bulge, superimposed on a disk with prominent spiral arms. ISO and Spitzer studies have shown that much of the scatter in the mid-infrared colors of spiral galaxies is related to
Sauvage, M. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
Submillimetre galaxies reside in dark matter haloes with masses greater than 3×1011 solar masses
The extragalactic background light at far-infrared wavelengths comes from optically faint, dusty, star-forming galaxies in the Universe with star formation rates of a few hundred solar masses per year. These faint, submillimetre galaxies are challenging to study individually because of the relatively poor spatial resolution of far-infrared
Amblard, Alexandre et al.Fecha de publicación:
22011 -
SPIRE imaging of M 82: Cool dust in the wind and tidal streams
M 82 is a unique representative of a whole class of galaxies, starbursts with superwinds, in the Very Nearby Galaxy Survey with Herschel. In addition, its interaction with the M 81 group has stripped a significant portion of its interstellar medium from its disk. SPIRE maps now afford better characterization of the far-infrared emission from cool
Roussel, H. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
Redshift Determination and CO Line Excitation Modeling for the Multiply Lensed Galaxy HLSW-01
We report on the redshift measurement and CO line excitation of HERMES J105751.1+573027 (HLSW-01), a strongly lensed submillimeter galaxy discovered in Herschel/SPIRE observations as part of the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES). HLSW-01 is an ultra-luminous galaxy with an intrinsic far-infrared luminosity of L FIR = 1.4 × 1013 L
Scott, K. S. et al.Fecha de publicación:
52011 -
Radial distribution of gas and dust in spiral galaxies . The case of M 99 (NGC 4254) and M 100 (NGC 4321)
By combining Herschel-SPIRE data with archival Spitzer, H i , and CO maps, we investigate the spatial distribution of gas and dust in the two famous grand-design spirals M 99 and M 100 in the Virgo cluster. Thanks to the unique resolution and sensitivity of the Herschel-SPIRE photometer, we are for the first time able to measure the distribution
Pohlen, M. et al.Fecha de publicación:
72010 -
On the origin of M81 group extended dust emission
Galactic cirrus emission at far-infrared wavelengths affects many extragalactic observations. Separating this emission from that associated with extragalactic objects is both important and difficult. In this paper we discuss a particular case, the M81 group, and the identification of diffuse structures prominent in the infrared, but also detected
Davies, J. I. et al.Fecha de publicación:
112010 -
Modeling of the HerMES Submillimeter Source Lensed by a Dark Matter Dominated Foreground Group of Galaxies
We present the results of a gravitational lensing analysis of the bright z s = 2.957 submillimeter galaxy (SMG) HERMES found in the Herschel/SPIRE science demonstration phase data from the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) project. The high-resolution imaging available in optical and near-IR channels, along with CO emission
Gavazzi, R. et al.Fecha de publicación:
92011