General
Los objetivos principales de este proyecto son: 1) estudiar la estructura y la dinámica del interior solar, 2) ampliar este estudio a otros tipos de estrellas y 3) buqueda de planetas extrasolares utilizando métodos fotométricos y su caracterización con información complementaria (espectrometría).
Para alcanzar el primer objetivo, utilizamos la Heliosismología (análisis de los modos propios de oscilación solar), una técnica que nos permite inferir la estructura interna y la dinámica del Sol con gran precisión. Este proyecto abarca los diversos aspectos necesarios para alcanzar los objetivos mencionados: instrumentales y observacionales (con las redes internacionales BiSON y GONG que operan en el Observatorio del Teide), reducción, análisis e interpretación de datos (en particular, los instrumentos GOLF y VIRGO a bordo del satélite SoHO). Por último, se llevan a cabo desarrollos teóricos en técnicas de inversión.
Además, la Astrosismología aplica técnicas similares a otras estrellas para inferir su estado evolutivo, estructura interna y dinámica. Gracias a los datos fotométricos de alta calidad recopilados por las misiones espaciales CoRoT, Kepler y TESS, es posible extraer parámetros sísmicos globales para cientos de miles de estrellas, desde la secuencia principal hasta la fase de gigante roja. Los modelos de evolución estelar se utilizan para encontrar el modelo que mejor se ajusta a los observables (espectroscópicos y sísmicos), lo que proporciona la masa, el radio y la edad precisos de la estrella. En particular, los sistemas binarios proporcionan restricciones adicionales a estos modelos y, por lo tanto, permiten poner a prueba las complejidades de la física estelar interna.
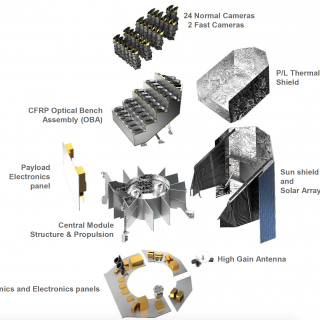
La caracterización precisa de los exoplanetas se fundamenta en un conocimiento preciso de la estrella anfitriona. En particular, se requiere una determinación fiable de su edad para limitar el estado evolutivo y la edad del sistema planetario, y para establecer límites sólidos sobre la habitabilidad a largo plazo. En la interfaz entre la asterosismología y la ciencia de los exoplanetas, se utiliza un modelo sísmico detallado de las estrellas anfitrionas para refinar las edades de los sistemas planetarios. Se garantiza una fuerte participación en la preparación de la misión PLATO de la ESA (lanzamiento previsto para finales de 2026), incluyendo la calibración de las curva de luz, las contribuciones al catálogo de calibración y validación científica (scvPIC), las propuestas de ciencia complementaria y las observaciones de seguimiento desde tierra.
Para este proyecto, son fundamentales las observaciones terrestres con las instalaciones observacionales a disposición de los investigadores del IAC, en particular en OCAN . Se están llevando a cabo observaciones continuas con los espectrógrafos terrestres de alta precisión de SONG y LCO para mejorar la caracterización espectroscópica y sísmica de las estrellas oscilantes e identificar sistemas binarios.
Miembros
Resultados
- Se ha publicado y producido una caracterización de última generación de las estrellas observadas por la misión Kepler en términos de su diagrama color-magnitude (CMD) y binariedad utilizando los datos de Gaia DR3 (Godoy-Rivera et al. 2026, A&A, 696, A243)
- En Grossmann et al. (2025, A&A, 696, A42) se emplearon estricciones astrosísmicas y de binariedad para modelar el sistema binario gigante roja KIC 9163796. Determinamos con éxito la edad del sistema con una precisión relativa inferior al 10 %, lo que demuestra la potencia de combinar ambos tipos de restricciones.
- Se ha publicado el estudio de la actividad magnética de más de 50 000 estrellas similares al Sol observadas por la misión Kepler (Mathur et al. 2025, ApJ, 982, 11). El análisis mostró diferentes comportamientos de la evolución de la actividad magnética según el tipo espectral. Este trabajo destaca que el nivel de actividad magnética del Sol es similar al de sus pares.
- Estudiamos la evolución fotométrica reciente de la nova recurrente simbiótica T CrB, cuya erupción es esperada con gran interés por la comunidad. Mostramos que los indicadores observacionales propuestos no predicen de forma fiable la explosión, que puede ocurrir incluso sin un precursor claro (Merc et al., MNRAS Letters, 541, L14).
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
Noticias