Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
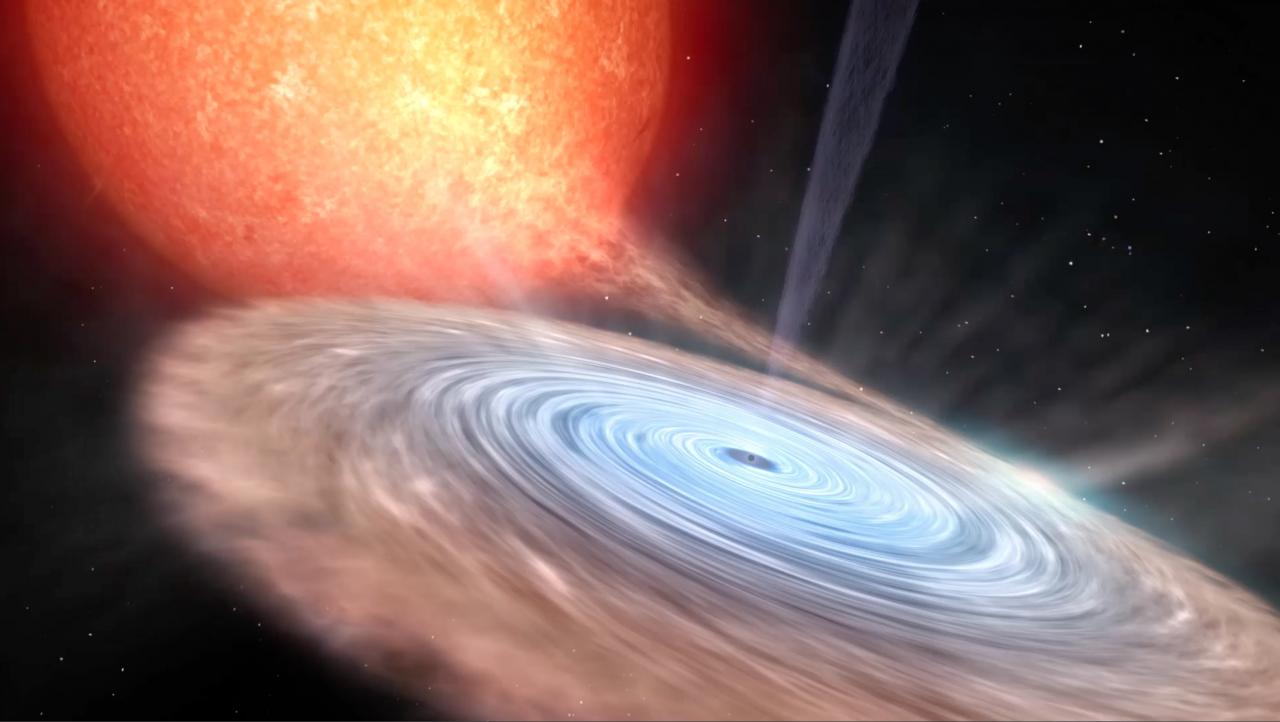
Los agujeros negros y estrellas de neutrones en binarias de rayos-X son laboratorios únicos para explorar la física de estos objetos compactos. No solo permiten confirmar la existencia de agujeros negros de origen estelar a través de mediciones dinámicas de sus masas, sino que también permiten investigar el comportamiento de la materia y la radiación bajo la influencia de un campo gravitatorio extremo. De este modo, es posible estudiar la física del proceso de acreción, la forma más eficiente de producción de energía conocida. El conocimiento de este proceso es esencial para entender el Universo, jugando un papel crucial en la astronomía galáctica y extra-galáctica.
Los objetivos científicos que se persiguen son:
- Estudios de acreción y eyección. Esta línea explota una fenomenología que nuestro grupo ha descubierto recientemente y se enfoca en la relación universal existente entre el proceso de acreción en agujeros negros y los procesos de expulsión en forma de jets colimados y vientos. Se pondrá énfasis en las propiedades generales y el efecto que el viento frío que hemos descubierto en binarias de rayos-X tiene sobre todo el proceso de acreción. Investigaremos como de comunes son estos vientos, como afectan al proceso de acrecimiento en el agujero negro y cuál es su relación con los jets y los vientos observados en rayos-X. Asimismo se realizarán estudios espectrales detallados en rayos X, con el fin de caracterizar los diferentes estados y geometrías de acreción en función de la luminosidad.
- Tenemos como objetivo definir la distribución de masas de agujeros negros estelares y estrellas de neutrones. Para ello medimos masas en binarias de rayos-X, continuando así nuestra ya reconocida contribución a uno de los experimentos fundamentales en la astrofísica moderna. De este modo, esperamos mejorar significativamente las distribuciones conocidas de objetos compactos, lo cual permitirá verificar modelos de explosión de supernovas y evolución de binarias compactas; además de obtener límites a la ecuación de estado de la materia nuclear. Para ello, mediremos las masas en binarias de rayos-X conocidas o recientemente descubiertas, e intentaremos encontrar un gran número de nuevas binarias de rayos X en nuestra galaxia que puedan después ser estudiadas dinámicamente.
- Analizar la estructura y variabilidad de los discos de acreción alrededor de los objetos compactos en diferentes bandas espectrales (óptico-rayos X). La distribución espectral durante la erupción (especialmente a altas energías) y su variación temporal es esencial para restringir los modelos de erupción y la estructura física del disco (e.g. radio del disco advectivo) así como la contribución del jet a la emisión en el visible y el infrarrojo.
Miembros
Resultados
- Nuestro equipo ha liderado un ambicioso estudio multi-frecuencia que cubrió las dos erupciones de 2015 del agujero negro transitorio V404 Cyg. Este evento ha sido uno de los más interesantes jamás observados de este tipo. En 2018 publicamos el trabajo global que recoge todos los datos espectroscópicos tomados en 1989 y 2015.
- Presentamos la evidencia de viento similar al detectado en V404 Cyg en un segundo sistema con agujero negro, V4641 Sgr.
- Se publicó tanto el artículo final como un estudio piloto sobre el método desarrollado por el grupo para descubrir y medir masas en agujeros negros en quietud. Esta técnica, potencialmente, podría triplicar la población conocida de estos objetos.
- Se medió la masa de la estrella de neutrones en PSR J2215+5135, una de las más masivas que se conocen hasta la fecha.
- Se presentó el primer estudio detallado del sistema ultra-compacto SLX 1737-282.
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
-
Fast infrared winds during the radio-loud and X-ray obscured stages of the black hole transient GRS 1915+105The black hole transient GRS 1915+105 entered a new phase of activity in 2018, generally characterised by low X-ray and radio fluxes. This phase has only been interrupted by episodes of strong and variable radio emission, where high levels of X-ray absorption local to the source were measured. We present 18 epochs of near-infrared spectroscopySánchez-Sierras, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122023 -
Hβ spectroscopy of the high-inclination black hole transient Swift J1357.2−0933 during quiescenceSwift J1357.2−0933 is a transient low-mass X-ray binary hosting a stellar-mass black hole. The source exhibits optical dips and very broad emission lines during both outburst and quiescence, which are thought to be the result of a high orbital inclination. We present phase-resolved spectroscopy obtained with the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTCCorral-Santana, J. M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112023 -
An infrared FWHM-K<SUB>2</SUB> correlation to uncover highly reddened quiescent black holesAmong the sample of Galactic transient X-ray binaries (SXTs) discovered to date, about 70 have been proposed as likely candidates to host a black hole. Yet, only 19 have been dynamically confirmed. Such a reliable confirmation requires phase-resolved spectroscopy of their companion stars, which is generally feasible when the system is in aCúneo, V. A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112023 -
Unveiling optical signatures of outflows in accreting white dwarfsAccreting white dwarfs are known to show signatures of wind-type outflows in the ultraviolet. However, at optical wavelengths, wind detections have only been reported for a few sources. We present GTC-10.4 m optical spectroscopy of four accreting white dwarfs (BZ Cam, V751 Cyg, MV Lyr, and V425 Cas) observed during luminous epochs, when theirCúneo, V. A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112023 -
The orbital period of the recurrent nova V2487 Oph revealedWe present the first reliable determination of the orbital period of the recurrent nova V2487 Oph (Nova Oph 1998). We derived a value of 0.753 ± 0.016 d (18.1 ± 0.4 h) from the radial velocity curve of the intense He II λ4686 emission line as detected in time-series X-shooter spectra. The orbital period is significantly shorter than earlier claimsRodríguez-Gil, Pablo et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122023 -
The orbital period, black hole mass, and distance to the X-ray transient GRS 1716-249 ( =N Oph 93)We present evidence for a 0.278(8) d ( =6.7 h) orbital period in the X-ray transient GRS 1716-249 (=N Oph 93), based on a superhump modulation detected during the 1995 mini-outburst plus ellipsoidal variability in quiescence. With a quiescent magnitude of r = 23.19 ± 0.15 N Oph 93 is too faint to warrant a full dynamical study through dedicatedCasares, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122023 -
UltraCompCAT: A comprehensive catalogue of ultra-compact and short orbital period X-ray binariesUltracompact X-ray binaries (UCXBs) are a distinctive but elusive family of low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs) characterised by their tight orbits and degenerate donor stars. Here we present UltraCompCAT, the first online and comprehensive catalogue of UCXBs. The initial version of UltraCompCAT comprises 49 sources, including 20 confirmed UCXBs (thoseArmas Padilla, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92023 -
Matter ejections behind the highs and lows of the transitional millisecond pulsar PSR J1023+0038Transitional millisecond pulsars are an emerging class of sources that link low-mass X-ray binaries to millisecond radio pulsars in binary systems. These pulsars alternate between a radio pulsar state and an active low-luminosity X-ray disc state. During the active state, these sources exhibit two distinct emission modes (high and low) thatBaglio, M. C. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92023 -
Sub-second infrared variability from the archetypal accreting neutron star 4U 1728-34We report on the first simultaneous high-time resolution X-ray and infrared (IR) observations of a neutron star low mass X-ray binary in its hard state. We performed $\approx 2\,$ h of simultaneous observations of 4U 1728-34 using HAWK-I@VLT, XMM-Newton, and NuSTAR. The source displayed significant X-ray and IR variability down to sub-second timeVincentelli, F. M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
102023 -
A 5.3-min-period pulsing white dwarf in a binary detected from radio to X-raysWhite dwarf stars are the most common stellar fossils. When in binaries, they make up the dominant form of compact object binary within the Galaxy and can offer insight into different aspects of binary formation and evolution. One of the most remarkable white dwarf binary systems identified to date is AR Scorpii (AR Sco). AR Sco is composed of an MPelisoli, Ingrid et al.
Fecha de publicación:
82023 -
An eclipsing 47 min double white dwarf binary at 400 pcWe present the discovery of the eclipsing double white dwarf (WD) binary WDJ 022558.21-692025.38 that has an orbital period of 47.19 min. Following identification with the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, we obtained time series ground based spectroscopy and high-speed multiband ULTRACAM photometry which indicate a primary DA WD of mass $0.40Munday, James et al.
Fecha de publicación:
102023 -
Dynamical mass of the white dwarf in XY Ari: a test for intermediate polar X-ray spectral modelsWe present a dynamical study of the eclipsing intermediate polar XY Ari based on time-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy obtained with the EMIR spectrograph on the 10.4-m Gran Telescopio Canarias. Using main sequence template spectra taken with the same instrument setup as the target spectra, we measure a radial velocity amplitude of the late K-Álvarez-Hernández, A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92023 -
Panning for gold, but finding helium: Discovery of the ultra-stripped supernova SN 2019wxt from gravitational-wave follow-up observationsWe present the results from multi-wavelength observations of a transient discovered during an intensive follow-up campaign of S191213g, a gravitational wave (GW) event reported by the LIGO-Virgo Collaboration as a possible binary neutron star merger in a low latency search. This search yielded SN 2019wxt, a young transient in a galaxy whose skyAgudo, I. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
72023 -
Ask the machine: systematic detection of wind-type outflows in low-mass X-ray binariesThe systematic discovery of outflows in the optical spectra of low-mass X-ray binaries opened a new avenue for the study of the outburst evolution in these extreme systems. However, the efficient detection of such features in a continuously growing data base requires the development of new analysis techniques with a particular focus on scalabilityMata Sánchez, D. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92023 -
GRB 201015A and the nature of low-luminosity soft gamma-ray burstsGRB 201015A is a peculiarly low luminosity, spectrally soft gamma-ray burst (GRB), with T 90 = 9.8 ± 3.5 s (time interval of detection of 90 per cent of photons from the GRB), and an associated supernova (likely to be type Ic or Ic-BL). GRB 201015A has an isotropic energy $E_{\gamma , \rm iso}$$= 1.75 ^{+0.60} _{-0.53} \times 10^{50}$ erg, andPatel, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
82023 -
The evolution of the UV/optical lag spectrum of NGC 7469 seen by the Liverpool TelescopeWe present the results regarding the analysis of an intensive monitoring of the Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN) NGC 7469. We observed the source for 4 months with almost daily cadence in the ugriz bands, using the IO:O on the Liverpool Telescope. We measured the lags with respect to the u band and found a clear change in the lag spectrum between theVincentelli, F. M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
52023 -
Optical and near-infrared spectroscopy of the black hole transient 4U 1543-47 during its 2021 ultra-luminous stateWe present simultaneous optical and near-infrared spectra obtained during the 2021 outburst of the black hole transient 4U 1543-47. The X-ray hardness-intensity diagram and the comparison with similar systems reveal a luminous outburst, probably reaching the Eddington luminosity, as well as a long-lasting excursion to the so-called ultra-luminousSánchez-Sierras, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
52023 -
The Fast X-Ray Transient XRT 210423 and Its Host GalaxyFast X-ray Transients (FXTs) are X-ray flares with durations ranging from a few hundred seconds to a few hours. Possible origins include the tidal disruption of a white dwarf by an intermediate-mass black hole, a supernova shock breakout, or a binary neutron star merger. We present the X-ray light curve and spectrum as well as deep optical imagingEappachen, D. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
52023 -
Multiwavelength observations of the extraordinary accretion event AT2021lwxWe present observations from X-ray to mid-infrared wavelengths of the most energetic non-quasar transient ever observed, AT2021lwx. Our data show a single optical brightening by a factor >100 to a luminosity of 7 × 10 45 erg s -1 and a total radiated energy of 1.5 × 10 53 erg, both greater than any known optical transient. The decline is smooth andWiseman, P. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
72023 -
Neutron star mass estimates from gamma-ray eclipses in spider millisecond pulsar binariesReliable neutron star mass measurements are key to determining the equation of state of cold nuclear matter, but such measurements are rare. Black widows and redbacks are compact binaries consisting of millisecond pulsars and semi-degenerate companion stars. Spectroscopy of the optically bright companions can determine their radial velocitiesClark, C. J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
42023
Charlas relacionadas
No se han encontrado charlas relacionadas.Congresos relacionados
No se han encontrado congresos relacionados.Noticias
-
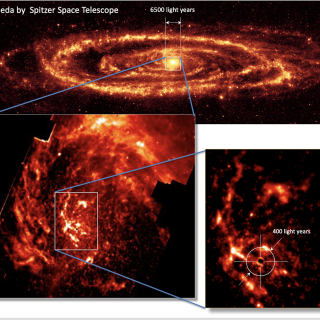 Observan cómo se alimenta el agujero negro de AndrómedaFecha de publicación
Observan cómo se alimenta el agujero negro de AndrómedaFecha de publicación -
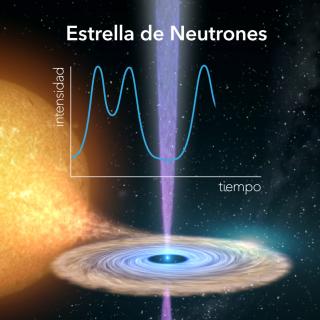 La erupción de una estrella de neutrones revela la naturaleza de fenómenos solo observados en agujeros negrosFecha de publicación
La erupción de una estrella de neutrones revela la naturaleza de fenómenos solo observados en agujeros negrosFecha de publicación -
 Descubren fuertes vientos templados durante la erupción de una estrella de neutronesFecha de publicación
Descubren fuertes vientos templados durante la erupción de una estrella de neutronesFecha de publicación



